Minimally invasive orthopedic surgery: arthroscopy
- PMID: 21765685
- PMCID: PMC3117522
Minimally invasive orthopedic surgery: arthroscopy
Abstract
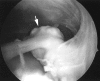
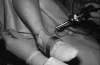
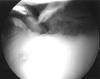
Arthroscopy, a minimally invasive alternative to standard open surgical techniques and now the most commonly performed orthopedic surgical procedure, was one of the greatest advances in orthopedic surgery of the 20(th) century. Minimally invasive surgeries result in less postoperative swelling than open techniques and reduce pain, risk of complications, and recovery times. Arthroscopy has evolved from a diagnostic tool to a therapeutic tool capable of treating a wide range of injuries and disorders. Many injuries, particularly those that at one time would have been career ending for athletes, can now be addressed with arthroscopy allowing a quicker return to full function. While arthroscopy has resulted in an overall decrease in morbidity compared with open techniques, it is still an invasive procedure and inherently involves risks. Almost all arthroscopic procedures can be performed in an outpatient setting. In 1999, 211 arthroscopic procedures were performed at Ochsner.
Figures

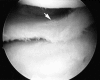
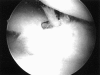
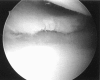
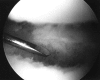



References
-
- Peltier L. F. Orthopedics. A History and Iconography. San Francisco: Norman Publishing, 1993.
-
- Watanabe M. Memories of the early days of arthroscopy. Arthroscopy. 1986;2:209–214. - PubMed
-
- Kreuscher P. H. Semilunar cartilage disease: A plea for the early recognition by means of the arthroscope and the early treatment of this condition. Illinois Medical Journal. 1931;47:290–292.
-
- Burman M. S. Arthroscopy or the direct visualization of joints: An experimental cadaver study. J Bone Joint Surg. 1931;13:669–695. - PubMed
-
- Watanabe M., Takeda S., Ikeuchi H. Atlas of Arthroscopy. Tokyo: Igaku-Shoin Ltd., 1957.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
