Transcriptional responses of cultured rat sympathetic neurons during BMP-7-induced dendritic growth
- PMID: 21765909
- PMCID: PMC3135585
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0021754
Transcriptional responses of cultured rat sympathetic neurons during BMP-7-induced dendritic growth
Abstract
Background: Dendrites are the primary site of synapse formation in the vertebrate nervous system; however, relatively little is known about the molecular mechanisms that regulate the initial formation of primary dendrites. Embryonic rat sympathetic neurons cultured under defined conditions extend a single functional axon, but fail to form dendrites. Addition of bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) triggers these neurons to extend multiple dendrites without altering axonal growth or cell survival. We used this culture system to examine differential gene expression patterns in naïve vs. BMP-treated sympathetic neurons in order to identify candidate genes involved in regulation of primary dendritogenesis.
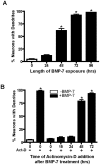
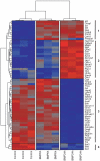
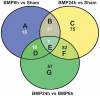
Methodology/principal findings: To determine the critical transcriptional window during BMP-induced dendritic growth, morphometric analysis of microtubule-associated protein (MAP-2)-immunopositive processes was used to quantify dendritic growth in cultures exposed to the transcription inhibitor actinomycin-D added at varying times after addition of BMP-7. BMP-7-induced dendritic growth was blocked when transcription was inhibited within the first 24 hr after adding exogenous BMP-7. Thus, total RNA was isolated from sympathetic neurons exposed to three different experimental conditions: (1) no BMP-7 treatment; (2) treatment with BMP-7 for 6 hr; and (3) treatment with BMP-7 for 24 hr. Affymetrix oligonucleotide microarrays were used to identify differential gene expression under these three culture conditions. BMP-7 significantly regulated 56 unique genes at 6 hr and 185 unique genes at 24 hr. Bioinformatic analyses implicate both established and novel genes and signaling pathways in primary dendritogenesis.
Conclusions/significance: This study provides a unique dataset that will be useful in generating testable hypotheses regarding transcriptional control of the initial stages of dendritic growth. Since BMPs selectively promote dendritic growth in central neurons as well, these findings may be generally applicable to dendritic growth in other neuronal cell types.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


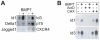
Similar articles
-
MicroRNAs are Necessary for BMP-7-induced Dendritic Growth in Cultured Rat Sympathetic Neurons.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2019 Oct;39(7):917-934. doi: 10.1007/s10571-019-00688-2. Epub 2019 May 18. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 31104181 Free PMC article.
-
Reactive oxygen species are involved in BMP-induced dendritic growth in cultured rat sympathetic neurons.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2015 Jul;67:116-25. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2015.06.007. Epub 2015 Jun 14. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26079955 Free PMC article.
-
Bone morphogenetic protein-5 (BMP-5) promotes dendritic growth in cultured sympathetic neurons.BMC Neurosci. 2001;2:12. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-2-12. Epub 2001 Sep 11. BMC Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11580864 Free PMC article.
-
Bone morphogenetic protein-7 enhances dendritic growth and receptivity to innervation in cultured hippocampal neurons.Eur J Neurosci. 2000 Jan;12(1):106-16. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9568.2000.00889.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2000. PMID: 10651865
-
Bone morphogenetic proteins.Growth Factors. 2004 Dec;22(4):233-41. doi: 10.1080/08977190412331279890. Growth Factors. 2004. PMID: 15621726 Review.
Cited by
-
BMP7-induced dendritic growth in sympathetic neurons requires p75(NTR) signaling.Dev Neurobiol. 2016 Sep;76(9):1003-13. doi: 10.1002/dneu.22371. Epub 2016 Jan 22. Dev Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 26663679 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs are Necessary for BMP-7-induced Dendritic Growth in Cultured Rat Sympathetic Neurons.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2019 Oct;39(7):917-934. doi: 10.1007/s10571-019-00688-2. Epub 2019 May 18. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 31104181 Free PMC article.
-
TGF-β Superfamily Regulation of Follicle-Stimulating Hormone Synthesis by Gonadotrope Cells: Is There a Role for Bone Morphogenetic Proteins?Endocrinology. 2019 Mar 1;160(3):675-683. doi: 10.1210/en.2018-01038. Endocrinology. 2019. PMID: 30715256 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reactive oxygen species are involved in BMP-induced dendritic growth in cultured rat sympathetic neurons.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2015 Jul;67:116-25. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2015.06.007. Epub 2015 Jun 14. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26079955 Free PMC article.
-
Gamma secretase activity modulates BMP-7-induced dendritic growth in primary rat sympathetic neurons.Auton Neurosci. 2023 Jul;247:103085. doi: 10.1016/j.autneu.2023.103085. Epub 2023 Apr 6. Auton Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37031474 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Purpura DP. Comparative physiology of dendrites. In: Quarton GC, Melnechuk T, Schmitt FO, editors. The Neurosciences: A Study Program. New York: Rockefeller University Press; 1967. pp. 372–393.
-
- Purves D. Body and Brain: A Trophic Theory of Neural Connections. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press; 1988. - PubMed
-
- Miller JP, Jacobs GA. Relationships between neuronal structure and function. J Exp Biol. 1984;112:129–145. - PubMed
-
- Schuman EM. Synapse specificity and long-term information storage. Neuron. 1997;18:339–342. - PubMed

