Extension of lifespan in C. elegans by naphthoquinones that act through stress hormesis mechanisms
- PMID: 21765926
- PMCID: PMC3135594
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0021922
Extension of lifespan in C. elegans by naphthoquinones that act through stress hormesis mechanisms
Abstract
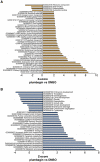
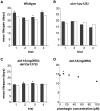
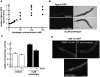
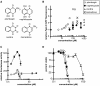
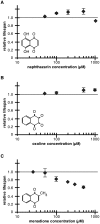
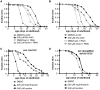
Hormesis occurs when a low level stress elicits adaptive beneficial responses that protect against subsequent exposure to severe stress. Recent findings suggest that mild oxidative and thermal stress can extend lifespan by hormetic mechanisms. Here we show that the botanical pesticide plumbagin, while toxic to C. elegans nematodes at high doses, extends lifespan at low doses. Because plumbagin is a naphthoquinone that can generate free radicals in vivo, we investigated whether it extends lifespan by activating an adaptive cellular stress response pathway. The C. elegans cap'n'collar (CNC) transcription factor, SKN-1, mediates protective responses to oxidative stress. Genetic analysis showed that skn-1 activity is required for lifespan extension by low-dose plumbagin in C. elegans. Further screening of a series of plumbagin analogs identified three additional naphthoquinones that could induce SKN-1 targets in C. elegans. Naphthazarin showed skn-1dependent lifespan extension, over an extended dose range compared to plumbagin, while the other naphthoquinones, oxoline and menadione, had differing effects on C. elegans survival and failed to activate ARE reporter expression in cultured mammalian cells. Our findings reveal the potential for low doses of naturally occurring naphthoquinones to extend lifespan by engaging a specific adaptive cellular stress response pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
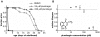
References
-
- Finkel T, Holbrook NJ. Oxidants, oxidative stress and the biology of ageing. Nature. 2000;408:239–247. - PubMed
-
- Kregel KC, Zhang HJ. An integrated view of oxidative stress in aging: basic mechanisms, functional effects, and pathological considerations. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2007;292:R18–36. - PubMed
-
- Head E, Liu J, Hagen TM, Muggenburg BA, Milgram NW, et al. Oxidative damage increases with age in a canine model of human brain aging. J Neurochem. 2002;82:375–381. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

