Zinc finger structure-function in Ikaros Marvin A Payne
- PMID: 21765982
- PMCID: PMC3135863
- DOI: 10.4331/wjbc.v2.i6.161
Zinc finger structure-function in Ikaros Marvin A Payne
Abstract
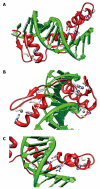
The zinc finger motif was used as a vehicle for the initial discovery of Ikaros in the context of T-cell differentiation and has been central to all subsequent analyses of Ikaros function. The Ikaros gene is alternately spliced to produce several isoforms that confer diversity of function and consequently have complicated analysis of the function of Ikaros in vivo. Key features of Ikaros in vivo function are associated with six C2H2 zinc fingers; four of which are alternately incorporated in the production of the various Ikaros isoforms. Although no complete structures are available for the Ikaros protein or any of its family members, considerable evidence has accumulated about the structure of zinc fingers and the role that this structure plays in the functions of the Ikaros family of proteins. This review summarizes the structural aspects of Ikaros zinc fingers, individually, and in tandem to provide a structural context for Ikaros function and to provide a structural basis to inform the design of future experiments with Ikaros and its family members.
Keywords: C2H2; DNA binding protein; Ikaros; Tandem; Transcription factor IIIA; Zinc finger.
Figures


References
-
- Georgopoulos K, Moore DD, Derfler B. Ikaros, an early lymphoid-specific transcription factor and a putative mediator for T cell commitment. Science. 1992;258:808–812. - PubMed
-
- Klug A. The discovery of zinc fingers and their development for practical applications in gene regulation and genome manipulation. Q Rev Biophys. 2010;43:1–21. - PubMed
-
- Kim CA, Berg JM. A 2.2 A resolution crystal structure of a designed zinc finger protein bound to DNA. Nat Struct Biol. 1996;3:940–945. - PubMed
-
- Klug A, Schwabe JW. Protein motifs 5. Zinc fingers. FASEB J. 1995;9:597–604. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

