Presence of caffeic acid in flaxseed lignan macromolecule
- PMID: 21766213
- PMCID: PMC3156902
- DOI: 10.1007/s11130-011-0245-1
Presence of caffeic acid in flaxseed lignan macromolecule
Abstract
Phenolic compounds were extracted from defatted flaxseeds using ethanol-dioxane (1:1, v/v). The crude extract obtained was purified using Amberlite XAD-16 column chromatography with water and methanol as mobile phases. RP-HPLC and SE-HPLC showed a lignan macromolecule (LM) as a dominant phenolic compound in the purified extract. After the alkaline hydrolysis of LM caffeic acid glucoside (CaAG) was isolated using a semi-preparative HPLC and its structure was confirmed by LC-ESI-MS. In LM of the investigated flaxseed, one molecule of caffeic acid corresponded with five molecules of p-coumaric acid and two molecules of ferulic acid. The presence of caffeic acid in the lignan molecule might be very beneficial due to its high antioxidant activity.
Figures
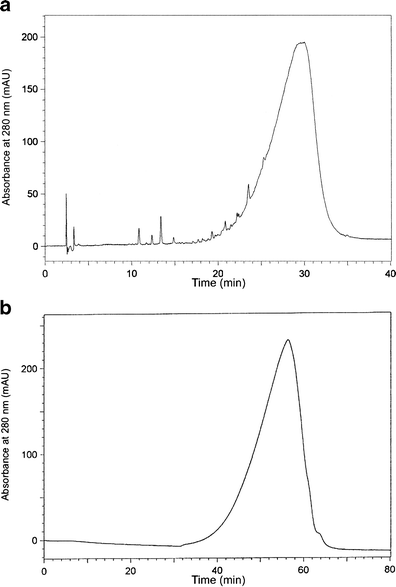
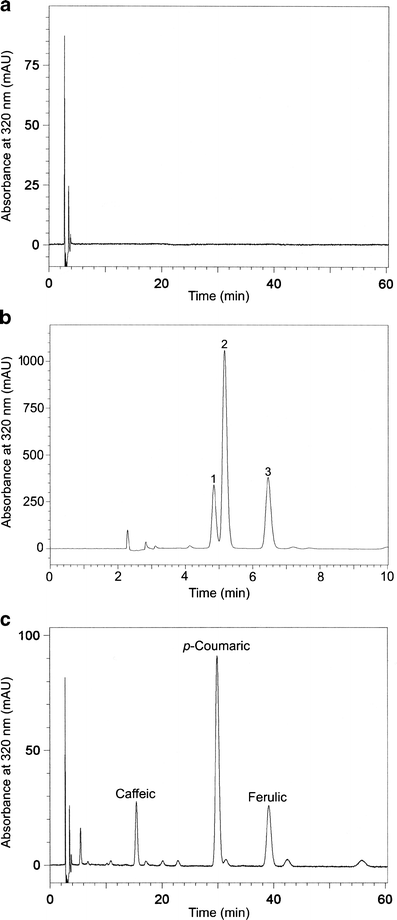

References
-
- Liu Z, Sarrinen NM, Thompson LU. Sesamin is one of the major precursor of mammalian lignans in sesame seed (Sesamum indicum) as observed in vitro and in rats. J Nutr. 2006;136:906–912. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

