Pseudoglycosyltransferase catalyzes nonglycosidic C-N coupling in validamycin a biosynthesis
- PMID: 21766819
- PMCID: PMC3162038
- DOI: 10.1021/ja203574u
Pseudoglycosyltransferase catalyzes nonglycosidic C-N coupling in validamycin a biosynthesis
Abstract
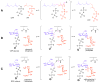
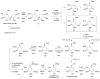
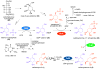
Glycosyltransferases are ubiquitous in nature. They catalyze a glycosidic bond formation between sugar donors and sugar or nonsugar acceptors to produce oligo/polysaccharides, glycoproteins, glycolipids, glycosylated natural products, and other sugar-containing entities. However, a trehalose 6-phosphate synthase-like protein has been found to catalyze an unprecedented nonglycosidic C-N bond formation in the biosynthesis of the aminocyclitol antibiotic validamycin A. This dedicated 'pseudoglycosyltransferase' catalyzes a condensation between GDP-valienol and validamine 7-phosphate to give validoxylamine A 7'-phosphate with net retention of the 'anomeric' configuration of the donor cyclitol in the product. The enzyme operates in sequence with a phosphatase, which dephosphorylates validoxylamine A 7'-phosphate to validoxylamine A.
© 2011 American Chemical Society
Figures



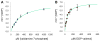
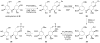
References
-
- Hansen SF, Bettler E, Rinnan A, Engelsen SB, Breton C. Mol Biosyst. 2010;6(10):1773–81. - PubMed
-
- Singh D, Seo MJ, Kwon HJ, Rajkarnikar A, Kim KR, Kim SO, Suh JW. Gene. 2006;376(1):13–23. - PubMed
-
- Wehmeier UF, Piepersberg W. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2004;63(6):613–25. - PubMed
-
- Rockser Y, Wehmeier UF. J Biotechnol. 2009;140(1–2):114–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

