Lymphotoxin controls the IL-22 protection pathway in gut innate lymphoid cells during mucosal pathogen challenge
- PMID: 21767811
- PMCID: PMC3375029
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chom.2011.06.002
Lymphotoxin controls the IL-22 protection pathway in gut innate lymphoid cells during mucosal pathogen challenge
Abstract
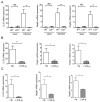
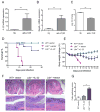
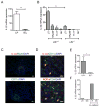
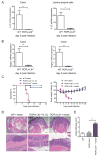
Innate lymphoid cells (ILCs) have emerged as important players, regulating the balance between protective immunity and immunopathology at mucosal surfaces. However, mechanisms that regulate ILCs' effector functions during mucosal pathogenic challenge are poorly defined. Using mice infected with the natural mouse enteric pathogen Citrobacter rodentium, we demonstrate that lymphotoxin (LT) is essential for IL-22 production by intestinal ILCs. Blocking of LTβR signaling dramatically reduced intestinal IL-22 production after C. rodentium infection. Conversely, stimulating LTβR signaling induced an IL-22 protection pathway in LT-deficient mice. Furthermore, exogenous IL-22 expression rescued LTβR-deficient mice. IL-22-producing ILCs were predominantly located in lymphoid follicles in the colon and interacted closely with dendritic cells (DCs). We find that an LT-driven positive feedback loop controls IL-22 production by RORγt(+) ILCs via LTβR signaling in DCs. Taken together, our data show that LTβR signaling in gut lymphoid follicles regulates IL-22 production by ILCs in response to mucosal pathogen challenge.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Comment in
-
Another armament in gut immunity: lymphotoxin-mediated crosstalk between innate lymphoid and dendritic cells.Cell Host Microbe. 2011 Jul 21;10(1):3-4. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2011.07.002. Cell Host Microbe. 2011. PMID: 21767806
Similar articles
-
Lymphotoxin-β receptor-independent development of intestinal IL-22-producing NKp46+ innate lymphoid cells.Eur J Immunol. 2011 Mar;41(3):780-6. doi: 10.1002/eji.201040851. Epub 2011 Feb 1. Eur J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21341264
-
The aryl hydrocarbon receptor regulates gut immunity through modulation of innate lymphoid cells.Immunity. 2012 Jan 27;36(1):92-104. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2011.11.011. Epub 2011 Dec 15. Immunity. 2012. PMID: 22177117 Free PMC article.
-
Lymphotoxin and the amazing technicolor circus of intestinal homeostasis.Mucosal Immunol. 2012 May;5(3):228-31. doi: 10.1038/mi.2012.3. Epub 2012 Feb 8. Mucosal Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22318496
-
Lymphotoxin organizes contributions to host defense and metabolic illness from innate lymphoid cells.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2014 Apr;25(2):227-33. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2013.12.007. Epub 2013 Dec 24. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2014. PMID: 24411493 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heterogeneity and diversity of group 3 innate lymphoid cells: new cells on the block.Int Immunol. 2016 Jan;28(1):29-34. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxv054. Epub 2015 Oct 13. Int Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26462712 Review.
Cited by
-
Intestinal fucose as a mediator of host-microbe symbiosis.J Immunol. 2015 Jun 15;194(12):5588-93. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1500395. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26048966 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Innate Lymphoid Cells and Inflammatory Bowel Disease.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022;1365:97-112. doi: 10.1007/978-981-16-8387-9_7. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022. PMID: 35567743 Review.
-
The IL-20 subfamily of cytokines--from host defence to tissue homeostasis.Nat Rev Immunol. 2014 Dec;14(12):783-95. doi: 10.1038/nri3766. Nat Rev Immunol. 2014. PMID: 25421700 Review.
-
LTβR-RelB signaling in intestinal epithelial cells protects from chemotherapy-induced mucosal damage.Front Immunol. 2024 May 30;15:1388496. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1388496. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38873613 Free PMC article.
-
Human Adipose Mesenchymal Stem Cell-derived Exosomes Protect Mice from DSS-Induced Inflammatory Bowel Disease by Promoting Intestinal-stem-cell and Epithelial Regeneration.Aging Dis. 2021 Sep 1;12(6):1423-1437. doi: 10.14336/AD.2021.0601. eCollection 2021 Sep. Aging Dis. 2021. PMID: 34527419 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Colonna M. Interleukin-22-producing natural killer cells and lymphoid tissue inducer-like cells in mucosal immunity. Immunity. 2009;31:15–23. - PubMed
-
- Cupedo T, Crellin NK, Papazian N, Rombouts EJ, Weijer K, Grogan JL, Fibbe WE, Cornelissen JJ, Spits H. Human fetal lymphoid tissue-inducer cells are interleukin 17-producing precursors to RORC+ CD127+ natural killer-like cells. Nat Immunol. 2009;10:66–74. - PubMed
-
- Eberl G, Littman DR. Thymic origin of intestinal alphabeta T cells revealed by fate mapping of RORgammat+ cells. Science. 2004;305:248–251. - PubMed
-
- Eberl G, Marmon S, Sunshine MJ, Rennert PD, Choi Y, Littman DR. An essential function for the nuclear receptor RORgamma(t) in the generation of fetal lymphoid tissue inducer cells. Nat Immunol. 2004;5:64–73. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

