Seasonal variation in TP53 R249S-mutated serum DNA with aflatoxin exposure and hepatitis B virus infection
- PMID: 21768053
- PMCID: PMC3226502
- DOI: 10.1289/ehp.1103539
Seasonal variation in TP53 R249S-mutated serum DNA with aflatoxin exposure and hepatitis B virus infection
Abstract
Background: Chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection and dietary aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) exposure are etiological factors for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in countries with hot, humid climates. HCC often harbors a TP53 (tumor protein p53) mutation at codon 249 (R249S). In chronic carriers, 1762T/1764A mutations in the HBV X gene are associated with increased HCC risk. Both mutations have been detected in circulating cell-free DNA (CFDNA) from asymptomatic HBV carriers.
Objective: We evaluated seasonal variation in R249S and HBV in relation to AFB1 exposure.
Methods: R249S was quantitated by mass spectrometry in CFDNA in a cross-sectional survey of 473 asymptomatic subjects (237 HBV carriers and 236 noncarriers) recruited in three villages in the Gambia over a 10-month period. 1762T/1764A HBV mutations were detected by quantitative polymerase chain reaction. In addition, the HBV S gene was sequenced in 99 subjects positive for HBV surface antigen (HBsAg).
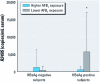
Results: We observed a seasonal variation of serum R249S levels. Positivity for R249S and average concentration were significantly higher in HBsAg-positive subjects surveyed during April-July (61%; 5,690 ± 11,300 R249S copies/mL serum) than in those surveyed October-March [32% and 480 ± 1,030 copies/mL serum (odds ratio = 3.59; 95% confidence interval: 2.05, 6.30; p < 0.001)]. Positivity for HBV e antigen (HBeAg) (a marker of HBV replication) and viral DNA load also varied seasonally, with 15-30% of subjects surveyed between April and June HBeAg positive, compared with < 10% surveyed during other months. We detected 1762T/1764A mutations in 8% of carriers, half of whom were positive for R249S. We found HBV genotype E in 95 of 99 HBsAg-positive subjects.
Conclusion: R249S is detectable in CFDNA of asymptomatic subjects. Evidence of temporal and quantitative variations suggests an interaction among AFB1 exposure, HBV positivity, and replication on TP53 mutation formation or persistence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare they have no actual or potential competing financial interests.
Figures
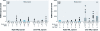

References
-
- Baptista M, Kramvis A, Kew MC. High prevalence of 1762T 1764A mutations in the basic core promoter of hepatitis B virus isolated from black Africans with hepatocellular carcinoma compared with asymptomatic carriers. Hepatology. 1999;29:946–953. - PubMed
-
- Chan KC, Leung SF, Yeung SW, Chan AT, Lo YM. Persistent aberrations in circulating DNA integrity after radiotherapy are associated with poor prognosis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14:4141–4145. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
