Human tryptase cleaves pro-nerve growth factor (pro-NGF): hints of local, mast cell-dependent regulation of NGF/pro-NGF action
- PMID: 21768088
- PMCID: PMC3173076
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.233486
Human tryptase cleaves pro-nerve growth factor (pro-NGF): hints of local, mast cell-dependent regulation of NGF/pro-NGF action
Abstract
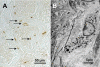
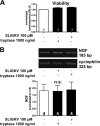
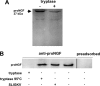
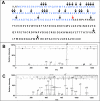
Several factors regulate nerve growth factor (NGF), which is formed from pro-NGF by intracellular and extracellular enzymatic cleavage. The close proximity between mast cells expressing the protease tryptase and NGF-producing smooth muscle-like peritubular cells in the testes of infertile patients led us to examine whether tryptase is among those factors. Human peritubular cells express functional tryptase receptors (PAR-2). Recombinant enzymatically active β-tryptase increased NGF levels in the culture medium of primary human peritubular cells, but the peptide agonist for PAR-2 (SLIGKV) did not. Neither tryptase nor the peptide increased NGF mRNA levels. To test whether the increase in NGF is due to enzymatic activity of tryptase acting on pro-NGF, supernatants of peritubular cells and synthetic pro-NGF were treated with tryptase. Results of Western blot studies indicate enzymatic cleavage of pro-NGF by active tryptase. Heat-inactivated tryptase or SLIGKV was not effective. Mass spectrometry analysis of in vitro cleavage products from recombinant tryptase and synthetic pro-NGF revealed multiple cleavage sites within the pro-NGF sequence. The results also indicate the generation of mature NGF and smaller NGF fragments as a result of tryptase action. Thus, tryptase-secreting mast cells in the vicinity of pro-NGF/NGF-secreting cells in any human tissue are likely able to alter the ratios of pro-NGF/NGF. As NGF and pro-NGF have different affinities for their receptors, this indicates a novel way by which mast cells, via tryptase, can modify the microenvironment in human tissues with regard to neurotrophin actions.
Figures
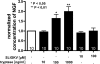

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

