Localization of In-111 antimyosin Fab and 99mTc-pyrophosphate in reperfusion myocardial infarction model
- PMID: 2176819
- PMCID: PMC4534996
- DOI: 10.3904/kjim.1990.5.1.15
Localization of In-111 antimyosin Fab and 99mTc-pyrophosphate in reperfusion myocardial infarction model
Abstract
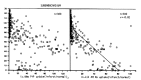
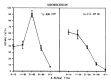
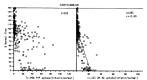
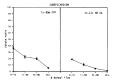
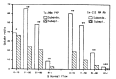
The myocardial uptake of In-111 antimyosin Fab and Tc-99m pyrophosphate was studied in dogs undergoing coronary artery occlusion for 90 minutes followed by reperfusion. The regional myocardial blood flow was determined by injecting Sc-46 labeled microsphere and was related to the relative concentrations of In-111 antimyosin and Tc-99m pyrophosphate. There was an inverse linear correlation between In-111 antimyosin Fab localization and the regional blood flow in both the subendocardial (r = 0.81) and subepicardial myocardium (r = -0.80). The greatest uptake of antimyosin was observed in areas of severe blood flow reduction (0-10% of normal). On the other hand, there was no correlation between the Tc-99m pyrophosphate uptake and the degree of blood flow reduction. Maximal subendocardial localization of Tc-99m degree of blood flow reduction. Maximal subendocardial localization of Tc-99m pyrophosphate was observed in areas where the blood flow was reduced to 31-50% of the normal. In the case of the subepicardium, the greatest uptake was localized to areas of 0 to 10% of the normal flow. In addition, there was significant myocardial uptake in regions where the blood flow was minimally reduced (greater than 81%). This study suggests that In-111 antimyosin Fab is a specific and quantitative tool in the evaluation of myocardial necrosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of indium-111 antimyosin antibody and technetium-99m pyrophosphate localization in reperfused and nonreperfused myocardial infarction.J Am Coll Cardiol. 1991 Feb;17(2):519-26. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(10)80125-1. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1991. PMID: 1846888
-
Myocardial damage delineated by indium-111 antimyosin Fab and technetium-99m pyrophosphate.J Nucl Med. 1987 Jan;28(1):76-82. J Nucl Med. 1987. PMID: 3025386
-
Localization of radiolabeled cardiac myosin-specific antibody in myocardial infarcts. Comparison with technetium-99m stannous pyrophosphate.Circulation. 1977 Jan;55(1):74-8. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.55.1.74. Circulation. 1977. PMID: 830221
-
Imaging necrotic myocardium: detection with 99mTc-pyrophosphate and radiolabeled antimyosin.Cardiol Clin. 1989 Aug;7(3):577-88. Cardiol Clin. 1989. PMID: 2548722 Review.
-
[Scintigraphy of "hot foci" in myocardial infarction while using technetium 99m labelled pyrophosphate and antimyosin antibodies labelled with radioactive indium 111].Pol Tyg Lek. 1991 May 6-20;46(19-21):386-8. Pol Tyg Lek. 1991. PMID: 1845680 Review. Polish.
References
-
- Coleman RE, Klevin MS, Ahmed SA, Weiss ES, Buchholz WM, Sobel BE. Mechanisms contributing to myocardial accumulation of technetium-99m stannous pyrophosphate after coronary arterial occlusion. Am J Cardiol. 1977;39:55. - PubMed
-
- Reimer KA, Martonffy K, Schumacher BL, Henkin RE, Quinn JL, III, Jennings RB. Localization of Tc-99m pyrophosphate and calcium in myocardial infarcts after temporary coronary occlusion in dogs. Proc Soc Exp Bio Med. 1977;156:272. - PubMed
-
- Poliner LR, Buja LM, Parkey RW, Bonte FJ, Willerson JT. Clinicopathologic finding in 52 patients studied by technetium-99m stannous pyrophosphate myocardial scintigraphy. Circulation. 1979;59:257. - PubMed
-
- Izquierdo C, Devous MD, Nicod P, Buja LM, Parkey RW, Bonte FJ, Willerson JT, Lewis SE. A comparison of infarct identification with technetium-99m pyrophosphate and staining with triphenyl tetrazolium chloride. J Nucl Med. 1983;24:492. - PubMed
-
- Mason JW, Myers RW, Alderman EL, Stinson EB, Goris ML, Kriss JP. Technetium-99m pyrophosphate myocardial uptake in patients with stable angina pectoris. Am J Cardiol. 1977;40:1. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
