Enhanced hemeoxygenase activity in the rostral ventrolateral medulla mediates exaggerated hemin-evoked hypotension in the spontaneously hypertensive rat
- PMID: 21768222
- PMCID: PMC3186288
- DOI: 10.1124/jpet.111.183368
Enhanced hemeoxygenase activity in the rostral ventrolateral medulla mediates exaggerated hemin-evoked hypotension in the spontaneously hypertensive rat
Abstract
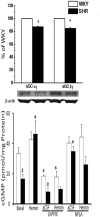
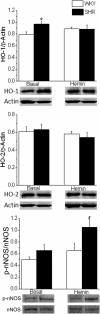
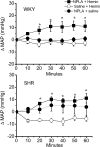
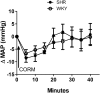
In anesthetized normotensive rats, activation of brainstem hemeoxygenase (HO) elicits sympathoinhibition and hypotension. Accordingly, we tested the hypothesis that attenuated basal or induced HO activity in the rostral ventrolateral medulla (RVLM) contributes to hypertension in the spontaneously hypertensive rat (SHR). We measured basal RVLM HO expression and catalytic activity and investigated the effects of intra-RVLM HO activation (hemin) or selective HO isoform 1 (HO-1) inhibition [zinc protoporphyrin IX (ZnPPIX)] on mean arterial pressure (MAP), heart rate, and RVLM neuronal norepinephrine (NE) level (index of sympathetic activity) in conscious SHRs and Wistar Kyoto rats. Basal RVLM HO catalytic activity (bilirubin level) and HO-1 expression were significantly higher in the SHR. These neurochemical findings were corroborated by the significantly greater decreases (hemin) and increases (ZnPPIX) in RVLM NE and MAP in the SHR. By contrast, HO-independent CO release in the RVLM (CO-releasing molecule 3) elicited similar MAP reductions in both rat strains. Furthermore, pretreatment with ZnPPIX or the selective neuronal nitric-oxide synthase (nNOS) inhibitor N-propyl-l-arginine abrogated the neurochemical (RVLM cGMP) and hypotensive responses caused by hemin. In addition to demonstrating, for the first time, higher basal RVLM HO catalytic activity and HO-1 expression in the SHR, the findings suggest: 1) the exaggerated hypotension elicited by intra-RVLM HO activation in the SHR is nNOS-dependent, and 2) in the SHR, the enhanced RVLM HO-nNOS signaling compensates for the reduced expression/activity of the downstream target, soluble guanylyl cyclase. Together, the findings suggest a protective role for the RVLM HO-nNOS pathway against further increases in MAP in the SHR.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Spontaneously hypertensive rats have more orexin neurons in the hypothalamus and enhanced orexinergic input and orexin 2 receptor-associated nitric oxide signalling in the rostral ventrolateral medulla.Exp Physiol. 2015 Sep;100(9):993-1007. doi: 10.1113/EP085016. Epub 2015 Jul 27. Exp Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26096870
-
Cystathionine-β-Synthase Gene Transfer Into Rostral Ventrolateral Medulla Exacerbates Hypertension via Nitric Oxide in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats.Am J Hypertens. 2015 Sep;28(9):1106-13. doi: 10.1093/ajh/hpu299. Epub 2015 Jan 26. Am J Hypertens. 2015. PMID: 25628417
-
Carbon monoxide regulates blood pressure cooperatively with nitric oxide in hypertensive rats.Heart Vessels. 2002 Jul;16(5):189-95. doi: 10.1007/s003800200020. Heart Vessels. 2002. PMID: 12181592
-
Age-related alterations in soluble guanylyl cyclase and cGMP pathway in spontaneously hypertensive rats.J Hypertens. 2003 Jun;21(6):1117-24. doi: 10.1097/00004872-200306000-00011. J Hypertens. 2003. PMID: 12777948
-
Enhancement of rostral ventrolateral medulla neuronal nitric-oxide synthase-nitric-oxide signaling mediates the central cannabinoid receptor 1-evoked pressor response in conscious rats.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2012 Jun;341(3):579-86. doi: 10.1124/jpet.112.192369. Epub 2012 Feb 24. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2012. PMID: 22366659 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Enhanced catabolism to acetaldehyde in rostral ventrolateral medullary neurons accounts for the pressor effect of ethanol in spontaneously hypertensive rats.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2012 Feb 1;302(3):H837-44. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00958.2011. Epub 2011 Dec 9. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22159996 Free PMC article.
-
Alcohol suppresses cardiovascular diurnal variations in male normotensive rats: Role of reduced PER2 expression and CYP2E1 hyperactivity in the heart.Alcohol. 2020 Dec;89:27-36. doi: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2020.08.001. Epub 2020 Aug 7. Alcohol. 2020. PMID: 32777474 Free PMC article.
-
Differential modulation of brainstem phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 signaling underlies WIN55,212-2 centrally mediated pressor response in conscious rats.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2012 Jan;340(1):11-8. doi: 10.1124/jpet.111.186858. Epub 2011 Sep 26. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2012. PMID: 21946192 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced vascular neuronal nitric-oxide synthase-derived nitric-oxide production underlies the pressor response caused by peripheral N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor activation in conscious rats.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2012 Aug;342(2):461-71. doi: 10.1124/jpet.112.194464. Epub 2012 May 11. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2012. PMID: 22580349 Free PMC article.
-
Restoration of Rostral Ventrolateral Medulla Cystathionine-γ Lyase Activity Underlies Moxonidine-Evoked Neuroprotection and Sympathoinhibition in Diabetic Rats.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2018 Feb;364(2):170-178. doi: 10.1124/jpet.117.243865. Epub 2017 Nov 13. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2018. PMID: 29133386 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Burke PG, Li Q, Costin ML, McMullan S, Pilowsky PM, Goodchild AK. (2008) Somatostatin 2A receptor-expressing presympathetic neurons in the rostral ventrolateral medulla maintain blood pressure. Hypertension 52:1127–1133 - PubMed
-
- Carraway MS, Ghio AJ, Taylor JL, Piantadosi CA. (1998) Induction of ferritin and heme oxygenase-1 by endotoxin in the lung. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 275:L583–L592 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

