Structural basis for complement factor I control and its disease-associated sequence polymorphisms
- PMID: 21768352
- PMCID: PMC3150940
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1102167108
Structural basis for complement factor I control and its disease-associated sequence polymorphisms
Abstract
The complement system is a key component of innate and adaptive immune responses. Complement regulation is critical for prevention and control of disease. We have determined the crystal structure of the complement regulatory enzyme human factor I (fI). FI is in a proteolytically inactive form, demonstrating that it circulates in a zymogen-like state despite being fully processed to the mature sequence. Mapping of functional data from mutants of fI onto the structure suggests that this inactive form is maintained by the noncatalytic heavy-chain allosterically modulating activity of the light chain. Once the ternary complex of fI, a cofactor and a substrate is formed, the allosteric inhibition is released, and fI is oriented for cleavage. In addition to explaining how circulating fI is limited to cleaving only C3b/C4b, our model explains the molecular basis of disease-associated polymorphisms in fI and its cofactors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
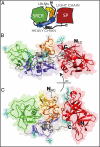
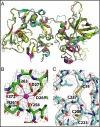

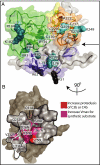

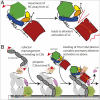
References
-
- Lachmann PJ, Müller-Eberhard HJ. The demonstration in human serum of “conglutinogen-activating factor” and its effect on the third component of complement. J Immunol. 1968;100:691–698. - PubMed
-
- Harris CL, Morgan BP. Complement Regulatory Proteins. London: Academic; 1999.
-
- van Lookeren Campagne M, Wiesmann C, Brown EJ. Macrophage complement receptors and pathogen clearance. Cell Microbiol. 2007;9:2095–2102. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

