Clinical and biologic features predictive of survival after relapse of neuroblastoma: a report from the International Neuroblastoma Risk Group project
- PMID: 21768459
- PMCID: PMC3158599
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2010.34.3392
Clinical and biologic features predictive of survival after relapse of neuroblastoma: a report from the International Neuroblastoma Risk Group project
Abstract
Purpose: Survival after neuroblastoma relapse is poor. Understanding the relationship between clinical and biologic features and outcome after relapse may help in selection of optimal therapy. Our aim was to determine which factors were significantly predictive of postrelapse overall survival (OS) in patients with recurrent neuroblastoma--particularly whether time from diagnosis to first relapse (TTFR) was a significant predictor of OS.
Patients and methods: Patients with first relapse/progression were identified in the International Neuroblastoma Risk Group (INRG) database. Time from study enrollment until first event and OS time starting from first event were calculated. Cox regression models were used to calculate the hazard ratio of increased death risk and perform survival tree regression. TTFR was tested in a multivariable Cox model with other factors.
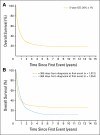
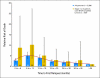
Results: In the INRG database (N = 8,800), 2,266 patients experienced first progression/relapse. Median time to relapse was 13.2 months (range, 1 day to 11.4 years). Five-year OS from time of first event was 20% (SE, ± 1%). TTFR was statistically significantly associated with OS time in a nonlinear relationship; patients with TTFR of 36 months or longer had the lowest risk of death, followed by patients who relapsed in the period of 0 to less than 6 months or 18 to 36 months. Patients who relapsed between 6 and 18 months after diagnosis had the highest risk of death. TTFR, age, International Neuroblastoma Staging System stage, and MYCN copy number status were independently predictive of postrelapse OS in multivariable analysis.
Conclusion: Age, stage, MYCN status, and TTFR are significant prognostic factors for postrelapse survival and may help in the design of clinical trials evaluating novel agents.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest and author contributions are found at the end of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Barker LM, Pendergrass TW, Sanders JE, et al. Survival after recurrence of Ewing's sarcoma family of tumors. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:4354–4362. - PubMed
-
- Dantonello T, Int-Veen C, Winkler P, et al. Initial patient characteristics can predict pattern and risk of relapse in localized rhabdomyosarcoma. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:406–413. - PubMed
-
- Malempati S, Gaynon P, Sather H, et al. Outcome after relapse among children with standard-risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Children's Oncology Group study CCG-1952. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:5800–5807. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

