Characterization of OXA-181, a carbapenem-hydrolyzing class D beta-lactamase from Klebsiella pneumoniae
- PMID: 21768505
- PMCID: PMC3186949
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00481-11
Characterization of OXA-181, a carbapenem-hydrolyzing class D beta-lactamase from Klebsiella pneumoniae
Abstract
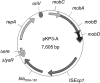
Klebsiella pneumoniae KP3 was isolated from a patient transferred from India to the Sultanate of Oman. K. pneumoniae KP3 was resistant to all β-lactams, including carbapenems, and expressed the carbapenem-hydrolyzing β-lactamase OXA-181, which differs from OXA-48 by four amino acid substitutions. Compared to OXA-48, OXA-181 possessed a very similar hydrolytic profile. The bla(OXA-181) gene was located on a 7.6-kb ColE-type plasmid and was linked to the insertion sequence ISEcp1. The ISEcp1-mediated one-ended transposition of bla(OXA-181) was also demonstrated.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

