Dopamine synthesis capacity before onset of psychosis: a prospective [18F]-DOPA PET imaging study
- PMID: 21768612
- PMCID: PMC3682447
- DOI: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2011.11010160
Dopamine synthesis capacity before onset of psychosis: a prospective [18F]-DOPA PET imaging study
Abstract
Objective: While there is robust evidence of elevated dopamine synthesis capacity once a psychotic disorder has developed, little is known about whether it is altered prior to the first episode of frank illness. The authors addressed this issue by measuring dopamine synthesis capacity in individuals at ultra-high risk of psychosis and then following them to determine their clinical outcome.
Method: This prospective study included 30 patients who met standard criteria for being at ultra-high risk of psychosis and 29 healthy volunteers. Participants were scanned using [(18)F]6-fluoro-L-dopa positron emission tomography. The ultra-high-risk patients were scanned at presentation and followed up for at least 3 years to determine their clinical outcome. Six patients had comorbid schizotypal personality disorder and were excluded from the analysis (data are provided for comparison). Of the remaining patients, nine developed a psychotic disorder (psychotic transition group) and 15 did not (nontransition group).
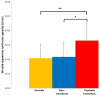
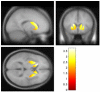
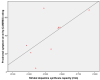
Results: There was a significant effect of group on striatal dopamine synthesis capacity. The psychotic transition group had greater dopamine synthesis capacity in the striatum (effect size=1.18) and its associative subdivision (effect size=1.24) than did the healthy comparison subjects and showed a positive correlation between dopamine synthesis capacity and symptom severity. Dopamine synthesis capacity was also significantly greater in the psychotic transition group than in the nontransition group.
Conclusions: These findings provide evidence that the onset of frank psychosis is preceded by presynaptic dopaminergic dysfunction. Further research is needed to determine the specificity of elevated dopamine synthesis capacity to particular psychotic disorders.
Figures

Comment in
-
Dopamine: a marker of psychosis and final common driver of schizophrenia psychosis.Am J Psychiatry. 2011 Dec;168(12):1239-40. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2011.11091346. Am J Psychiatry. 2011. PMID: 22193666 No abstract available.
References
-
- Abi-Dargham A. Do we still believe in the dopamine hypothesis? New data bring new evidence. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2004;7:S1–S5. - PubMed
-
- Davis KL, Kahn RS, Ko G, Davidson M. Dopamine in schizophrenia: a review and reconceptualization. Am J Psychiatry. 1991;148:1474–1486. - PubMed
-
- Laruelle M, Abi-Dargham A. Dopamine as the wind of the psychotic fire: new evidence from brain imaging studies. J Psychopharmacol. 1999;13:358–371. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

