Role of β4 integrin phosphorylation in human invasive squamous cell carcinoma: regulation of hemidesmosome stability modulates cell migration
- PMID: 21769085
- PMCID: PMC3184203
- DOI: 10.1038/labinvest.2011.104
Role of β4 integrin phosphorylation in human invasive squamous cell carcinoma: regulation of hemidesmosome stability modulates cell migration
Abstract
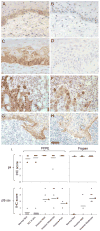
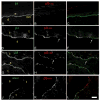
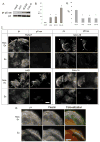
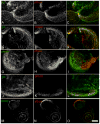
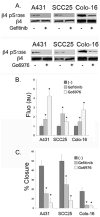
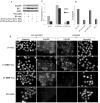
Hemidesmosomes (HDs) are multiprotein structures that anchor epithelia to the basement membrane. During squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) invasion, there is a reduction in the number of HDs, which may facilitate dissemination. Mechanisms of HD disassembly are incompletely understood. Previous work has shown that epidermal growth factor (EGF)-induced phosphorylation of the β4 integrin on three of its serines, S(1356)S(1360)S(1364), can induce HD disassembly in normal cells. Here, we examine the role of β4 integrin serine phosphorylation in SCC. We have found that around 60% of invasive cutaneous SCC show increased β4 phosphorylation on S(1356) when compared with carcinoma in situ or normal tissue. To assess the mechanisms by which SCC increases β4 phosphorylation, we performed in vitro analyses. Compared with keratinocytes, SCC cells showed increased levels of S(1356) phosphorylation in the absence of EGF, correlating with reduced HD-like structures. In addition, phospho-S(1356) signal was largely segregated from other HD components. Epidermal growth factor receptor and PKC inhibitors inhibited basal levels of S(1356) phosphorylation in SCC, suggesting that cells use intrinsic mechanisms to activate the EGF signaling pathway to induce β4 phosphorylation. Moreover, these inhibitors stabilized HD-like structures in SCC cells and reduced their migratory ability. Mutation of S(1356)S(1360)S(1364) in SCC cells to non-phosphorylatable alanines stabilized HD-like structures and substantially reduced migration, while mutation into phosphorylation mimicking aspartate reduced HD-like structures but had no effect on migration, suggesting that serine phosphorylation function is releasing anchorage rather than promoting migration. Altogether these results suggest that β4 serine phosphorylation may have an important role during SCC invasion by destabilizing HDs and facilitating migration.
© 2011 USCAP, Inc All rights reserved
Figures

Similar articles
-
The calcium/calcineurin pathway promotes hemidesmosome stability through inhibition of β4 integrin phosphorylation.J Biol Chem. 2012 Sep 21;287(39):32440-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.385245. Epub 2012 Aug 3. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22865863 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of a novel site on the {beta}4 integrin at the trailing edge of migrating cells promotes hemidesmosome disassembly.Mol Biol Cell. 2009 Jan;20(1):56-67. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e08-06-0646. Epub 2008 Nov 12. Mol Biol Cell. 2009. PMID: 19005215 Free PMC article.
-
EGF-induced MAPK signaling inhibits hemidesmosome formation through phosphorylation of the integrin {beta}4.J Biol Chem. 2010 Nov 26;285(48):37650-62. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.138818. Epub 2010 Sep 24. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20870721 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of hemidesmosome disassembly by growth factor receptors.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2008 Oct;20(5):589-96. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2008.05.001. Epub 2008 Jun 24. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18583123 Review.
-
Integrin beta4, keratinocytes and papillomavirus infection.Int J Mol Med. 2006 Feb;17(2):195-202. Int J Mol Med. 2006. PMID: 16391815 Review.
Cited by
-
SYK interaction with ITGβ4 suppressed by Epstein-Barr virus LMP2A modulates migration and invasion of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells.Oncogene. 2015 Aug 20;34(34):4491-9. doi: 10.1038/onc.2014.380. Epub 2014 Dec 22. Oncogene. 2015. PMID: 25531330
-
Molecular architecture and function of the hemidesmosome.Cell Tissue Res. 2015 May;360(2):363-78. doi: 10.1007/s00441-014-2061-z. Epub 2014 Dec 9. Cell Tissue Res. 2015. PMID: 25487405 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The calcium/calcineurin pathway promotes hemidesmosome stability through inhibition of β4 integrin phosphorylation.J Biol Chem. 2012 Sep 21;287(39):32440-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.385245. Epub 2012 Aug 3. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22865863 Free PMC article.
-
Palmitoylation by DHHC3 is critical for the function, expression, and stability of integrin α6β4.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012 Jul;69(13):2233-44. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-0924-6. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012. PMID: 22314500 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of the origin of oral squamous cell carcinoma by microarray analysis: Squamous epithelium or minor salivary gland?Int J Cancer. 2018 Nov 15;143(10):2551-2560. doi: 10.1002/ijc.31811. Epub 2018 Sep 21. Int J Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30121960 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alam M, Ratner D. Cutaneous squamous-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2001;344(13):975–983. - PubMed
-
- Scully C, Bagan J. Oral squamous cell carcinoma overview. Oral Oncol. 2009;45(4–5):301–308. - PubMed
-
- Green KJ, Jones JCR. Desmosomes and hemidesmosomes - structure and function of molecular components[Review] FASEB Journal. 1996;10(8):871–881. - PubMed
-
- Borradori L, Sonnenberg A. Hemidesmosomes: roles in adhesion, signaling and human diseases. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1996;8(5):647–656. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

