Use of Prothrombin Complex Concentrate for Vitamin K Antagonist Reversal before Surgical Treatment of Intracranial Hemorrhage
- PMID: 21769259
- PMCID: PMC3096433
- DOI: 10.4137/CCRep.S6433
Use of Prothrombin Complex Concentrate for Vitamin K Antagonist Reversal before Surgical Treatment of Intracranial Hemorrhage
Abstract
Background: Oral anticoagulant therapy (OAT) is used to prevent/treat thromboembolism. Major bleeding is common in patients on OAT; eg, warfarin increases intracranial hemorrhage (ICH) risk.
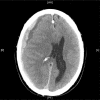
Case: A 71-year-old male on warfarin (to reduce stroke risk) presented at Accident and Emergency Minor Injuries Unit with headache after reportedly sounding 'drunk'. On triage, the patient appeared lucid and well. However, International Normalized Ratio (INR) was 4.1. Head computed tomography (CT) indicated a large right-sided subdural hematoma. Prothrombin complex concentrate (PCC; Beriplex(®) P/N, CSL Behring) with vitamin K normalized the INR within minutes of administration. The patient underwent neurosurgery without complications, and was discharged after 5 days, with no residual neurological symptoms.
Conclusions: ICH patients can present with no neurological signs. In OAT patients with headache, INR must be established; if ≥3.0, normalization of INR and head CT are essential. PCC is the best option to rapidly reverse anticoagulation and correct INR pre-surgery.
Keywords: Beriplex® P/N; International Normalized Ratio; anticoagulation reversal; computed tomography; intracranial hemorrhage; prothrombin complex concentrate.
Figures


References
-
- Evans G, Luddington R, Baglin T. Beriplex P/N reverses severe warfarin-induced overanticoagulation immediately and completely in patients presenting with major bleeding. Br J Haematol. 2001;115(4):998–1001. - PubMed
-
- Baglin TP, Cousins D, Keeling DM, Perry DJ, Watson HG. Safety indicators for inpatient and outpatient oral anticoagulant care: [corrected] Recommendations from the British Committee for Standards in Haematology and National Patient Safety Agency. Br J Haematol. 2007;136(1):26–9. - PubMed
-
- Appelboam R, Thomas EO. Warfarin and intracranial haemorrhage. Blood Rev. 2009;23(1):1–9. - PubMed
-
- Hart RG, Boop BS, Anderson DC. Oral anticoagulants and intracranial hemorrhage. Facts and hypotheses. Stroke. 1995;26(8):1471–7. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

