Small molecule inhibitors of human papillomavirus protein - protein interactions
- PMID: 21769307
- PMCID: PMC3137155
- DOI: 10.2174/1874357901105010080
Small molecule inhibitors of human papillomavirus protein - protein interactions
Abstract
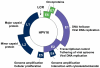
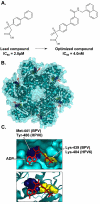
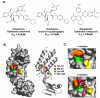
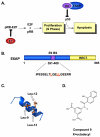
Human papillomaviruses (HPV) have now been identified as a necessary cause of benign and malignant lesions of the differentiating epithelium, particularly cervical cancer, the second most prevalent cancer in women worldwide. While two prophylactic HPV vaccines and screening programs are available, there is currently no antiviral drug for the treatment of HPV infections and associated diseases. The recent progress toward the identification and characterization of specific molecular targets for small molecule-based approaches provides prospect for the development of effective HPV antiviral compounds. Traditionally, antiviral therapies target viral enzymes. HPV encode for few proteins, however, and rely extensively on the infected cell for completion of their life cycle. This article will review the functions of the viral E1 helicase, which encodes the only enzymatic function of the virus, of the E2 regulatory protein, and of the viral E6 and E7 oncogenes in viral replication and pathogenesis. Particular emphasis will be placed on the recent progress made towards the development of novel small molecule inhibitors that specifically target and inhibit the functions of these viral proteins, as well as their interactions with other viral and/or cellular proteins.
Keywords: E1; E2; E6; E6AP.; HPV; cervical cancer; protein interaction; small molecule inhibitor.
Figures

References
-
- de Villiers EM, Fauquet C, Broker TR, Bernard HU, zur Hausen H. Classification of papillomaviruses. Virology. 2004;324:17–27. - PubMed
-
- Woodman CB, Collins SI, Young LS. The natural history of cervical HPV infection: unresolved issues. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007;7:11–22. - PubMed
-
- Gillison ML. Human papillomavirus-associated head and neck cancer is a distinct epidemiologic, clinical, and molecular entity. Semin Oncol. 2004;31:744–54. - PubMed
-
- Syrjanen S. Human papillomavirus (HPV) in head and neck cancer. J Clin Virol. 2005;32(Suppl 1):S59–66. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
