A one-year, phase I/IIa, open-label pilot trial of imatinib mesylate in the treatment of systemic sclerosis-associated active interstitial lung disease
- PMID: 21769849
- PMCID: PMC3205223
- DOI: 10.1002/art.30548
A one-year, phase I/IIa, open-label pilot trial of imatinib mesylate in the treatment of systemic sclerosis-associated active interstitial lung disease
Abstract
Objective: Transforming growth factor β (TGFβ) and platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) may play a critical role in systemic sclerosis (SSc)-related interstitial lung disease (ILD), and imatinib is a potent inhibitor of TGFβ and PDGF production. In this 1-year, phase I/IIa open-label pilot study of imatinib in patients with SSc-related active ILD, our primary aim was to assess the safety of imatinib; we also explored its efficacy.
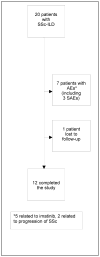
Methods: We recruited 20 SSc patients with a forced vital capacity (FVC) of <85% predicted, dyspnea on exertion, and presence of a ground-glass appearance on high-resolution computed tomography. Patients received oral therapy with imatinib (up to 600 mg/day) for a period of 1 year. Adverse events were recorded, pulmonary function was tested, and the modified Rodnan skin thickness score (MRSS) was assessed every 3 months. The course of changes in lung function, the Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ) disability index (DI), and the MRSS were modeled over the period of study to explore treatment efficacy.
Results: The majority of patients were female (65%), Caucasian (75%), and had diffuse cutaneous SSc (70%). At baseline, the mean ± SD FVC % predicted was 65.2 ± 14.0 and the mean ± SD MRSS was 18.7 ± 10.1. The mean ± SD dosage of imatinib was 445 ± 125 mg/day. Of the 20 SSc patients, 12 completed the study, 7 discontinued because of adverse events (AEs), and 1 patient was lost to followup. Common AEs (≥20%) included fatigue, facial/lower extremity edema, nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, generalized rash, and new-onset proteinuria. Treatment with imatinib showed a trend toward improvement in the FVC % predicted (1.74%; P not significant) and the MRSS (3.9 units; P < 0.001).
Conclusion: Use of high-dose daily therapy with imatinib (600 mg/day) in SSc patients with ILD was associated with a large number of AEs. Our experience with AEs suggests that dosages of imatinib lower than 600 mg/day may be appropriate and that further dose ranging analysis is needed in order to understand the therapeutic index of imatinib in SSc.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00512902.
Copyright © 2011 by the American College of Rheumatology.
Figures
Comment in
-
Tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy for systemic sclerosis: Quo Vadis?Arthritis Rheum. 2011 Nov;63(11):3199-203. doi: 10.1002/art.30545. Arthritis Rheum. 2011. PMID: 21769846 No abstract available.
References
-
- Beon M, Harley RA, Wessels A, Silver RM, Ludwicka-Bradley A. Myofibroblast induction and microvascular alteration in scleroderma lung fibrosis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2004;22(6):733–42. - PubMed
-
- Corrin B, Butcher D, McAnulty BJ, duBois RM, Black CM, Laurent GJ, et al. Immunohistochemical localization of transforming growth factor-beta 1 in the lungs of patients with systemic sclerosis, cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis and other lung disorders. Histopathology. 1994;24(2):145–50. - PubMed
-
- Horan GS, Wood S, Ona V, Li DJ, Lukashev ME, Weinreb PH, et al. Partial inhibition of integrin alpha(v)beta6 prevents pulmonary fibrosis without exacerbating inflammation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008;177(1):56–65. - PubMed
-
- Trojanowska M. Role of PDGF in fibrotic diseases and systemic sclerosis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2008;47 (Suppl 5):v2–v4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical