Motor neuron impairment mediated by a sumoylated fragment of the glial glutamate transporter EAAT2
- PMID: 21769946
- PMCID: PMC3896305
- DOI: 10.1002/glia.21218
Motor neuron impairment mediated by a sumoylated fragment of the glial glutamate transporter EAAT2
Abstract
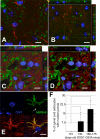
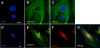
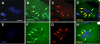
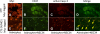
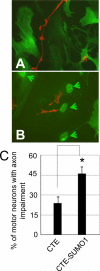
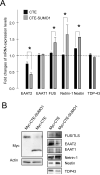
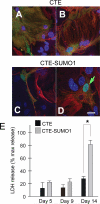
Dysregulation of glutamate handling ensuing downregulation of expression and activity levels of the astroglial glutamate transporter EAAT2 is implicated in excitotoxic degeneration of motor neurons in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). We previously reported that EAAT2 (a.k.a. GLT-1) is cleaved by caspase-3 at its cytosolic carboxy-terminus domain. This cleavage results in impaired glutamate transport activity and generates a proteolytic fragment (CTE) that we found to be post-translationally conjugated by SUMO1. We show here that this sumoylated CTE fragment accumulates in the nucleus of spinal cord astrocytes of the SOD1-G93A mouse model of ALS at symptomatic stages of disease. Astrocytic expression of CTE, artificially tagged with SUMO1 (CTE-SUMO1) to mimic the native sumoylated fragment, recapitulates the nuclear accumulation pattern of the endogenous EAAT2-derived proteolytic fragment. Moreover, in a co-culture binary system, expression of CTE-SUMO1 in spinal cord astrocytes initiates extrinsic toxicity by inducing caspase-3 activation in motor neuron-derived NSC-34 cells or axonal growth impairment in primary motor neurons. Interestingly, prolonged nuclear accumulation of CTE-SUMO1 is intrinsically toxic to spinal cord astrocytes, although this gliotoxic effect of CTE-SUMO1 occurs later than the indirect, noncell autonomous toxic effect on motor neurons. As more evidence on the implication of SUMO substrates in neurodegenerative diseases emerges, our observations strongly suggest that the nuclear accumulation in spinal cord astrocytes of a sumoylated proteolytic fragment of the astroglial glutamate transporter EAAT2 could participate to the pathogenesis of ALS and suggest a novel, unconventional role for EAAT2 in motor neuron degeneration.
Copyright © 2011 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Acarin L, Villapol S, Faiz M, Rohn TT, Castellano B, Gonzalez B. Caspase-3 activation in astrocytes following postnatal excitotoxic damage correlates with cytoskeletal remodeling but not with cell death or proliferation. Glia. 2007;55(9):954–65. - PubMed
-
- Bernardi R, Pandolfi PP. Structure, dynamics and functions of promyelocytic leukaemia nuclear bodies. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8(12):1006–16. - PubMed
-
- Blackburn D, Sargsyan S, Monk PN, Shaw PJ. Astrocyte function and role in motor neuron disease: a future therapeutic target? Glia. 2009;57(12):1251–64. - PubMed
-
- Boston-Howes W, Gibb SL, Williams EO, Pasinelli P, Brown RH, Jr., Trotti D. Caspase-3 cleaves and inactivates the glutamate transporter EAAT2. J Biol Chem. 2006;281(20):14076–84. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

