Dosimetric evaluation of Acuros XB Advanced Dose Calculation algorithm in heterogeneous media
- PMID: 21771317
- PMCID: PMC3168411
- DOI: 10.1186/1748-717X-6-82
Dosimetric evaluation of Acuros XB Advanced Dose Calculation algorithm in heterogeneous media
Abstract
Background: A study was realised to evaluate and determine relative figures of merit of a new algorithm for photon dose calculation when applied to inhomogeneous media.
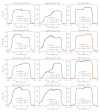
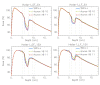
Methods: The new Acuros XB algorithm implemented in the Varian Eclipse treatment planning system was compared against a Monte Carlo method (VMC++), and the Analytical Anisotropic Algorithm (AAA). The study was carried out in virtual phantoms characterized by simple geometrical structures. An insert of different material and density was included in a phantom built of skeletal-muscle and HU = 0 (setting "A"): Normal Lung (lung, 0.198 g/cm3); Light Lung (lung, 0.035 g/cm3); Bone (bone, 1.798 g/cm3); another phantom (setting "B") was built of adipose material and including thin layers of bone (1.85 g/cm3), adipose (0.92 g/cm3), cartilage (1.4745 g/cm3), air (0.0012 g/cm3). Investigations were performed for 6 and 15 MV photon beams, and for a large (13 × 13 cm2) and a small (2.8 × 13 cm2) field.
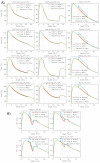
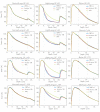
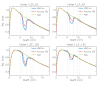
Results: Results are provided in terms of depth dose curves, transverse profiles and Gamma analysis (3 mm/3% and 2 mm/2% distance to agreement/dose difference criteria) in planes parallel to the beam central axis; Monte Carlo simulations were assumed as reference. Acuros XB gave an average gamma agreement, with a 3 mm/3% criteria, of 100%, 86% and 100% for Normal Lung, Light Lung and Bone settings, respectively, and dose to medium calculations. The same figures were 86%, 11% and 100% for AAA, where only dose rescaled to water calculations are possible.
Conclusions: In conclusion, Acuros XB algorithm provides a valid and accurate alternative to Monte Carlo calculations for heterogeneity management.
Figures
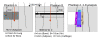



Similar articles
-
Dosimetric validation of Acuros XB with Monte Carlo methods for photon dose calculations.Med Phys. 2011 Apr;38(4):2208-21. doi: 10.1118/1.3567146. Med Phys. 2011. PMID: 21626955
-
Comparative evaluation of modern dosimetry techniques near low- and high-density heterogeneities.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2015 Sep 8;16(5):142–158. doi: 10.1120/jacmp.v16i5.5589. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2015. PMID: 26699322 Free PMC article.
-
On the dosimetric impact of inhomogeneity management in the Acuros XB algorithm for breast treatment.Radiat Oncol. 2011 Aug 26;6:103. doi: 10.1186/1748-717X-6-103. Radiat Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21871079 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization of the Eclipse TPS beam configuration parameters for small field dosimetry using Monte Carlo simulations and experimental measurements.Phys Med. 2023 Oct;114:103141. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmp.2023.103141. Epub 2023 Oct 30. Phys Med. 2023. PMID: 37820506 Review.
-
Evaluation of the effect of field sizes on radiation dose in the presence of metal materials using Monte Carlo simulation.Appl Radiat Isot. 2022 Apr;182:110143. doi: 10.1016/j.apradiso.2022.110143. Epub 2022 Feb 8. Appl Radiat Isot. 2022. PMID: 35152162 Review.
Cited by
-
Influence of optional measurement parameters in the Eclipse treatment planning system on the quality of the dosimetric model of the biomedical accelerator using the Acuros XB algorithm.Rep Pract Oncol Radiother. 2022 May 19;27(2):241-249. doi: 10.5603/RPOR.a2022.0019. eCollection 2022. Rep Pract Oncol Radiother. 2022. PMID: 36299384 Free PMC article.
-
Dose Calculation Accuracy of AAA and AcurosXB Algorithms for Small Central and Interface Lung Lesions - Verification with Gafchromic Film Dosimetry.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2018 Jan 27;19(1):253-259. doi: 10.22034/APJCP.2018.19.1.253. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2018. PMID: 29374410 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of six TPS algorithms in computing entrance and exit doses.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2014 May 8;15(3):229–240. doi: 10.1120/jacmp.v15i3.4739. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2014. PMID: 24892349 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the TG-43 formalism for intraoperative radiotherapy dosimetry in glioblastoma treatment.Med Phys. 2025 Jul;52(7):e17930. doi: 10.1002/mp.17930. Med Phys. 2025. PMID: 40661039 Free PMC article.
-
Synthetic computed tomography based dose calculation in prostate cancer patients with hip prostheses for magnetic resonance imaging-only radiotherapy.Phys Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2023 Jul 8;27:100469. doi: 10.1016/j.phro.2023.100469. eCollection 2023 Jul. Phys Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37520639 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fogliata A, Vanetti E, Albers D, Brink C, Clivio A, Knöös T, Nicolini G, Cozzi L. On the dosimetric behaviour of photon dose calculation algorithms in the presence of simple geometric heterogeneities: comparison with Monte Carlo calculations. Phys Med Biol. 2007;52:1363–1385. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/52/5/011. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

