SabR enhances nikkomycin production via regulating the transcriptional level of sanG, a pathway-specific regulatory gene in Streptomyces ansochromogenes
- PMID: 21771341
- PMCID: PMC3146816
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2180-11-164
SabR enhances nikkomycin production via regulating the transcriptional level of sanG, a pathway-specific regulatory gene in Streptomyces ansochromogenes
Abstract
Background: sabR is a pleiotropic regulatory gene which has been shown to positively regulate the nikkomycin biosynthesis and negatively affect the sporulation of Streptomyces ansochromogenes. In this study, we investigate the mechanism of SabR on modulating nikkomycin production in Streptomyces ansochromogenes.
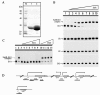
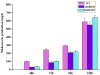
Results: The transcription start point of sabR was determined by high-resolution S1 nuclease mapping and localized at the nucleotide T at position 37 bp upstream of the potential sabR translation start codon (GTG). Disruption of sabR enhanced its own transcription, but retarded the nikkomycin production. Over-expression of sabR enhanced nikkomycin biosynthesis in Streptomyces ansochromogenes. EMSA analysis showed that SabR bound to the upstream region of sanG, but it did not bind to the upstream region of its encoding gene (sabR), sanF and the intergenic region between sanN and sanO. DNase 1 footprinting assays showed that the SabR-binding site upstream of sanG was 5'-CTTTAAGTCACCTGGCTCATTCGCGTTCGCCCAGCT-3' which was designated as SARE. Deletion of SARE resulted in the delay of nikkomycin production that was similar to that of sabR disruption mutant.
Conclusions: These results indicated that SabR modulated nikkomycin biosynthesis as an enhancer via interaction with the promoter region of sanG, and expanded our understanding about regulatory cascade in nikkomycin biosynthesis.
Figures


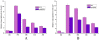

References
-
- Hopwood DA. Forty years of genetics with Streptomyces: from in vivo through in vitro to in silico. Microbiology. 1999;145:2183–2202. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

