Clinical analysis of stereotactic body radiation therapy using extracranial gamma knife for patients with mainly bulky inoperable early stage non-small cell lung carcinoma
- PMID: 21771344
- PMCID: PMC3151217
- DOI: 10.1186/1748-717X-6-84
Clinical analysis of stereotactic body radiation therapy using extracranial gamma knife for patients with mainly bulky inoperable early stage non-small cell lung carcinoma
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the clinical efficacy and toxicity of stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) using extracranial gamma knife in patients with mainly bulky inoperable early stage non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC).
Materials and methods: A total of 43 medically inoperable patients with mainly bulky Stage I/II NSCLC received SBRT using gamma knife were reviewed. The fraction dose and the total dose were determined by the radiation oncologist according to patients' general status, tumor location, tumor size and the relationship between tumor and nearby organ at risk (OAR). The total dose of 34~47.5 Gy was prescribed in 4~12 fractions, 3.5~10 Gy per fraction, one fraction per day or every other day. The therapeutic efficacy and toxicity were evaluated.
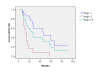
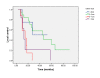
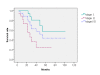
Results: The median follow-up was 22 months (range, 3-102 months). The local tumor response rate was 95.35%, with CR 18.60% (8/43) and PR 76.74% (33/43), respectively. The local control rates at 1, 2, 3, 5 years were 77.54%, 53.02%, 39.77%, and 15.46%, respectively, while the 1- and 2-year local control rates were 75% and 60% for tumor ≤3 cm; 84% and 71% for tumor sized 3~5 cm; 55% and 14.6% for tumor sized 5~7 cm; and 45%, 21% in those with tumor size of >7 cm. The overall survival rate at 1, 2, 3, 5 years were 92.04%, 78.04%, 62.76%, 42.61%, respectively. The toxicity of stereotactic radiation therapy was grade 1-2. Clinical stages were significantly important factor in local control of lung tumors (P = 0.000). Both clinical stages (P = 0.015) and chemotherapy (P = 0.042) were significantly important factors in overall survival of lung tumors.
Conclusion: SBRT is an effective and safe therapy for medically inoperable patients with early stage NSCLC. Clinical stage was the significant prognostic factors for both local tumor control and overall survival. The toxicity is mild. The overall local control for bulky tumors is poor. Tumor size is a poor prognostic factor, and the patients for adjuvant chemotherapy need to be carefully selected.
Figures
References
-
- Xiao Y, Papiez L, Paulus R, Timmerman R, Straube WL, Bosch WR, Michalski J, Galvin JM. Dosimetric evaluation of heterogeneity corrections for RTOG 0236: stereotactic body radiotherapy of inoperable stage I-II non-small-cell lung cancer. International Journal of Radiation Oncology, Biology, Physics. 2009;73:1235–1242. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2008.11.019. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Xia T, Li H, Sun Q, Wang Y, Fan N, Yu Y, Li P, Chang JY. Promising clinical outcome of stereotactic body radiation therapy for patients with inoperable Stage I/II non-small-cell lung cancer. International Journal of Radiation Oncology, Biology, Physics. 2006;66:117–125. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2006.04.013. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Silvano G. New radiation techniques for treatment of locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) Annals of Oncology. 2006;17 - PubMed
-
- Ricardi U, Filippi AR, Guarneri A, Giglioli FR, Ciammella P, Franco P, Mantovani C, Borasio P, Scagliotti GV, Ragona R. Stereotactic body radiation therapy for early stage non-small cell lung cancer: results of a prospective trial. Lung Cancer. 2010;68:72–77. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2009.05.007. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials