Experimental mapping of soluble protein domains using a hierarchical approach
- PMID: 21771856
- PMCID: PMC3185438
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkr548
Experimental mapping of soluble protein domains using a hierarchical approach
Abstract
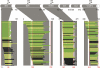
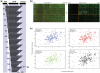
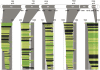
Exploring the function and 3D space of large multidomain protein targets often requires sophisticated experimentation to obtain the targets in a form suitable for structure determination. Screening methods capable of selecting well-expressed, soluble fragments from DNA libraries exist, but require the use of automation to maximize chances of picking a few good candidates. Here, we describe the use of an insertion dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) vector to select in-frame fragments and a split-GFP assay technology to filter-out constructs that express insoluble protein fragments. With the incorporation of an IPCR step to create high density, focused sublibraries of fragments, this cost-effective method can be performed manually with no a priori knowledge of domain boundaries while permitting single amino acid resolution boundary mapping. We used it on the well-characterized p85α subunit of the phosphoinositide-3-kinase to demonstrate the robustness and efficiency of our methodology. We then successfully tested it onto the polyketide synthase PpsC from Mycobacterium tuberculosis, a potential drug target involved in the biosynthesis of complex lipids in the cell envelope. X-ray quality crystals from the acyl-transferase (AT), dehydratase (DH) and enoyl-reductase (ER) domains have been obtained.
Figures



References
-
- Pedelacq JD, Piltch E, Liong EC, Berendzen J, Kim CY, Rho BS, Park MS, Terwilliger TC, Waldo GS. Engineering soluble proteins for structural genomics. Nat. Biotechnol. 2002;20:927–932. - PubMed
-
- Pedelacq JD, Cabantous S, Tran T, Terwilliger TC, Waldo GS. Engineering and characterization of a superfolder green fluorescent protein. Nat. Biotechnol. 2006;24:79–88. - PubMed
-
- Sippl MJ. Fold space unlimited. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2009;19:312–320. - PubMed
-
- Prodromou C, Savva R, Driscoll PC. DNA fragmentation-based combinatorial approaches to soluble protein expression Part I. Generating DNA fragment libraries. Drug Discov. Today. 2007;12:931–938. - PubMed
-
- Cornvik T, Dahlroth SL, Magnusdottir A, Herman MD, Knaust R, Ekberg M, Nordlund P. Colony filtration blot: a new screening method for soluble protein expression in Escherichia coli. Nat. Methods. 2005;2:507–509. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

