The effect of preterm birth on thalamic and cortical development
- PMID: 21772018
- PMCID: PMC3328341
- DOI: 10.1093/cercor/bhr176
The effect of preterm birth on thalamic and cortical development
Abstract
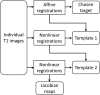
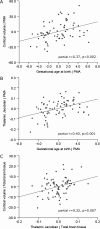
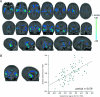
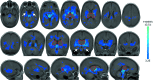
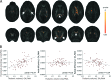
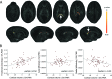
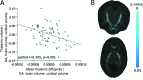
Preterm birth is a leading cause of cognitive impairment in childhood and is associated with cerebral gray and white matter abnormalities. Using multimodal image analysis, we tested the hypothesis that altered thalamic development is an important component of preterm brain injury and is associated with other macro- and microstructural alterations. T(1)- and T(2)-weighted magnetic resonance images and 15-direction diffusion tensor images were acquired from 71 preterm infants at term-equivalent age. Deformation-based morphometry, Tract-Based Spatial Statistics, and tissue segmentation were combined for a nonsubjective whole-brain survey of the effect of prematurity on regional tissue volume and microstructure. Increasing prematurity was related to volume reduction in the thalamus, hippocampus, orbitofrontal lobe, posterior cingulate cortex, and centrum semiovale. After controlling for prematurity, reduced thalamic volume predicted: lower cortical volume; decreased volume in frontal and temporal lobes, including hippocampus, and to a lesser extent, parietal and occipital lobes; and reduced fractional anisotropy in the corticospinal tracts and corpus callosum. In the thalamus, reduced volume was associated with increased diffusivity. This demonstrates a significant effect of prematurity on thalamic development that is related to abnormalities in allied brain structures. This suggests that preterm delivery disrupts specific aspects of cerebral development, such as the thalamocortical system.
Figures
References
-
- Ajayi-Obe M, Saeed N, Cowan FM, Rutherford MA, Edwards AD. Reduced development of cerebral cortex in extremely preterm infants. Lancet. 2000;356:1162–1163. - PubMed
-
- Allendoerfer KL, Shatz CJ. The subplate, a transient neocortical structure: its role in the development of connections between thalamus and cortex. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1994;17:185–218. - PubMed
-
- Anjari M, Counsell SJ, Srinivasan L, Allsop JM, Hajnal JV, Rutherford MA, Edwards AD. The association of lung disease with cerebral white matter abnormalities in preterm infants. Pediatrics. 2009;124:268–276. - PubMed
-
- Anjari M, Srinivasan L, Allsop JM, Hajnal JV, Rutherford MA, Edwards AD, Counsell SJ. Diffusion tensor imaging with tract-based spatial statistics reveals local white matter abnormalities in preterm infants. Neuroimage. 2007;35:1021–1027. - PubMed
-
- Arai Y, Deguchi K, Mizuguchi M, Takashima S. Expression of beta-amyloid precursor protein in axons of periventricular leukomalacia brains. Pediatr Neurol. 1995;13:161–163. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

