Repression of KIAA1199 attenuates Wnt-signalling and decreases the proliferation of colon cancer cells
- PMID: 21772334
- PMCID: PMC3170968
- DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2011.268
Repression of KIAA1199 attenuates Wnt-signalling and decreases the proliferation of colon cancer cells
Abstract
Background: The KIAA1199 transcript is upregulated in colon adenomas and downregulated upon β-catenin knockdown.
Methods: Transcript profiling was performed on >500 colon biopsies, methylation profiling data were compared with transcript data. Immunohistochemistry assessed KIAA1199 protein expression in 270 stage II/III tumours (>3 years follow-up). The effects of stable KIAA1199 knockdown in SW480 cells (three different constructs) were studied using transcriptional profiling, proliferation and protein analysis.
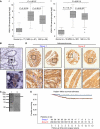
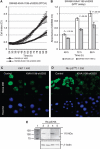
Results: The KIAA1199 transcript was strongly upregulated in 95% of adenocarcinomas. Absent expression in normal mucosa correlated with KIAA1199 promotor methylation. Nuclear and cytoplasmic KIAA1199 protein expression was identified in colon adenocarcinomas and other types of cancers. A subpopulation of patients with tumours strongly expressing KIAA1199 in the nucleus showed a better outcome with regard to recurrence as lung or liver metastases. The KIAA1199 knockdown affected the cell cycle and the Wnt-signalling pathway. Reduced cellular proliferation and decreased KI67, phosphorylated retinoblastoma, β-catenin and ASCL2 protein expression supported these findings. Eighteen Wnt-signalling genes differentially expressed upon KIAA1199 knockdown correlated with the KIAA1199 expression profile in clinical specimens.
Conclusion: The KIAA1199 knockdown attenuates the effects of the Wnt/β-catenin signalling and it may thus be regarded as a regulatory part of this pathway.
Figures

References
-
- Abe S, Usami S, Nakamura Y (2003) Mutations in the gene encoding KIAA1199 protein, an inner-ear protein expressed in Deiters’ cells and the fibrocytes, as the cause of nonsyndromic hearing loss. J Hum Genet 48(11): 564–570 - PubMed
-
- Bienz M, Clevers H (2000) Linking colorectal cancer to Wnt signaling. Cell 103(2): 311–320 - PubMed
-
- Birkenkamp-Demtroder K, Christensen LL, Olesen SH, Frederiksen CM, Laiho P, Aaltonen LA, Laurberg S, Sorensen FB, Hagemann R, Orntoft TF (2002) Gene expression in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res 62(15): 4352–4363 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

