P63 and Ki-67 expression in trophoblastic disease and spontaneous abortion
- PMID: 21772911
- PMCID: PMC3129081
P63 and Ki-67 expression in trophoblastic disease and spontaneous abortion
Abstract
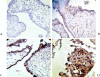
Background: Despite well-described histopathologic criteria, the distinction of spontaneous abortion from hydatidiform mole and complete hydatidiform mole from partial hydatidiform mole remains a problem because of interobserver and intraobserver variability. The aim of this study was to evaluate the value of two immunohistochemical markers in the differential diagnosis of subgroups of lesions of villous trophoblasts and spontaneous abortions.
Methods: Immunohistochemistry with the P63 and Ki-67 antibody was performed in formalin-fixed paraffinembedded samples of non hydropic abortion (n = 14), partial hydatidiform mole (n = 12), complete hydatidiform mole (n = 12) and choriocarcinoma (n = 12). The Ki-67 and P63 labeling index (number of positive nuclei/total number of nuclei) for villous stromal cells, cytotrophoblasts and syncytiotrophoblasts were evaluated separately by counting 100 cells of each population. Statistical analysis was carried out by χ(2) analysis, and the Mann-Whitney U test. Statistical significance was determined at p < 0.05 on the basis of 2-tailed tests.
Results: None of nonhydropic spontaneous abortions analyzed exhibited positive cytotrotrophoblastic and syncytiotrophoblastic cells for P63. The syncytiotrophoblastic cells were negative for p63 in all of choriocarcinomas. All of choriocarcinomas analyzed exhibited severe expression of Ki-67 in cytotrotrophoblastic cells. None of abortions and partial moles was diffusely labeled with Ki-67.
Conclusions: Ki-67 labeling index in cytotrophoblastic cells is the best index to differentiate between abortion and subgroups of lesions of villous trophoblasts as well as between different subgroups of lesions of villous trophoblasts. Ki-67 is a better marker than P63 to attain this goal.
Keywords: Abortion; Choriocarcinoma; Complete Hydatidiform Mole; Immunohistochemistry; Ki-67; P63; Partial Hydatidiform Mole.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors have no conflict of interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ki-67 expression in hydatidiform moles and hydropic abortions.Iran Red Crescent Med J. 2013 Jul;15(7):590-4. doi: 10.5812/ircmj.5348. Epub 2013 Jul 5. Iran Red Crescent Med J. 2013. PMID: 24396579 Free PMC article.
-
P63 expression in hydropic abortion and gestational trophoblastic diseases.Placenta. 2006 Jun-Jul;27(6-7):740-3. doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2005.05.006. Epub 2005 Jul 18. Placenta. 2006. PMID: 16026831
-
[Immunohistochemistry of p57 and p53 protein in differential diagnosis of hydropic abortion, partial and complete hydatidiform mole].Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 2011 Oct;40(10):694-7. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 2011. PMID: 22321550 Chinese.
-
Immunohistochemical characterization of p57Kip2 expression in tetraploid hydropic placentas.Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2004 Aug;128(8):897-900. doi: 10.5858/2004-128-897-ICOPEI. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2004. PMID: 15270611 Review.
-
Pathology of gestational trophoblastic diseases.Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2003 Dec;17(6):849-68. doi: 10.1016/s1521-6934(03)00094-4. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2003. PMID: 14614885 Review.
Cited by
-
Diagnostic value of P63 in differentiating normal gestation from molar pregnancy.J Res Med Sci. 2013 Jun;18(6):462-6. J Res Med Sci. 2013. PMID: 24250692 Free PMC article.
-
Ki-67 expression in hydatidiform moles and hydropic abortions.Iran Red Crescent Med J. 2013 Jul;15(7):590-4. doi: 10.5812/ircmj.5348. Epub 2013 Jul 5. Iran Red Crescent Med J. 2013. PMID: 24396579 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular and Immunohistochemical Characteristics of Complete Hydatidiform Moles.Balkan J Med Genet. 2017 Jun 30;20(1):27-34. doi: 10.1515/bjmg-2017-0009. eCollection 2017 Jun 30. Balkan J Med Genet. 2017. PMID: 28924538 Free PMC article.
-
[Histopathology and clinical aspects of extrauterine pregnancy].Pathologe. 2018 Sep;39(5):431-444. doi: 10.1007/s00292-018-0471-5. Pathologe. 2018. PMID: 30135973 Review. German.
References
-
- Lage JM, Mark SD, Roberts DJ, Goldstein DP, Bernstein MR, Berkowitz RS. A flow cytometric study of 137 fresh hydropic placentas: correlation between types of hydatidiform moles and nuclear DNA ploidy. Obstet Gynecol. 1992;79(3):403–10. - PubMed
-
- Paradinas FJ, Browne P, Fisher RA, Foskett M, Bagshawe KD, Newlands E. A clinical, histopathological and flow cytometric study of 149 complete moles, 146 partial moles and 107 non-molar hydropic abortions. Histopathology. 1996;28(2):101–9. - PubMed
-
- Fukunaga M, Endo Y, Ushigome S. Flow cytometric and clinicopathologic study of 197 hydatidiform moles with special reference to the significance of cytometric aneuploidy and literature review. Cytometry. 1995;22(2):135–8. - PubMed
-
- Coukos G, Makrigiannakis A, Chung J, Randall TC, Rubin SC, Benjamin I. Complete hydatidiform mole.A disease with a changing profile. J Reprod Med. 1999;44(8):698–704. - PubMed
-
- Li HW, Tsao SW, Cheung AN. Current understandings of the molecular genetics of gestational trophoblastic diseases. Placenta. 2002;23(1):20–31. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
