Conformational-dependent and independent RNA binding to the fragile x mental retardation protein
- PMID: 21772992
- PMCID: PMC3136132
- DOI: 10.4061/2011/246127
Conformational-dependent and independent RNA binding to the fragile x mental retardation protein
Abstract
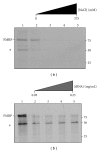
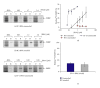
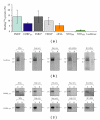
The interaction between the fragile X mental retardation protein (FMRP) and BC1 RNA has been the subject of controversy. We probed the parameters of RNA binding to FMRP in several ways. Nondenaturing agarose gel analysis showed that BC1 RNA transcripts produced by in vitro transcription contain a population of conformers, which can be modulated by preannealing. Accordingly, FMRP differentially binds to the annealed and unannealed conformer populations. Using partial RNase digestion, we demonstrate that annealed BC1 RNA contains a unique conformer that FMRP likely binds. We further demonstrate that this interaction is 100-fold weaker than that the binding of eEF-1A mRNA and FMRP, and that preannealing is not a general requirement for FMRP's interaction with RNA. In addition, binding does not require the N-terminal 204 amino acids of FMRP, methylated arginine residues and can be recapitulated by both fragile X paralogs. Altogether, our data continue to support a model in which BC1 RNA functions independently of FMRP.
Figures


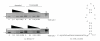

References
-
- Bagni C, Greenough WT. From mRNP trafficking to spine dysmorphogenesis: the roots of fragile X syndrome. Nature Reviews Neuroscience. 2005;6(5):376–387. - PubMed
-
- Bardoni B, Davidovic L, Bensaid M, Khandjian EW. The fragile X syndrome: exploring its molecular basis and seeking a treatment. Expert Reviews in Molecular Medicine. 2006;8(8):1–16. - PubMed
-
- Jin P, Warren ST. New insights into fragile X syndrome: from molecules to neurobehaviors. Trends in Biochemical Sciences. 2003;28(3):152–158. - PubMed
-
- O’Donnell WT, Warren ST. A decade of molecular studies of fragile X syndrome. Annual Review of Neuroscience. 2002;25:315–338. - PubMed
-
- Mercaldo V, Descalzi G, Zhuo M. Fragile X mental retardation protein in learning-related synaptic plasticity. Molecules and Cells. 2009;28(6):501–507. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

