Physicochemical characterization and dissolution properties of meloxicam-gelucire 50/13 binary systems
- PMID: 21773073
- PMCID: PMC3134858
- DOI: 10.3797/scipharm.1101-22
Physicochemical characterization and dissolution properties of meloxicam-gelucire 50/13 binary systems
Abstract
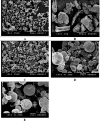
A solid dispersion of Meloxicam (MX), a poorly soluble, non steroidal anti-inflammatory drug, and Gelucire 50/13 was prepared by spray drying. Spherical microparticles were yielded with smooth surfaces as observed by scanning electron microscopy. According to differential scanning calorimetry and powder X-ray diffractometry analysis, MX was transformed from the crystalline state to the amorphous state as confirmed by the disappearance of its melting peak and the crystalline peaks. The dissolution tests at pH 7.4 revealed that the dissolution rate of encapsulated MX was 2.5-fold higher than that of the corresponding physical mixture and fourfold higher than the drug alone, respectively. The microparticles prepared at a ratio of 1:4 (drug/Gelucire) exhibited a 4-fold higher anti-inflammatory activity on the paw edema of rats in comparison to the drug alone. All in all, this work reveals that spray drying is a suitable technique for preparation of solid dispersions with improved biopharmaceutical and pharmacological characteristics of MX.
Keywords: Anti-inflammatory activity; Dissolution; Meloxicam; Powder X-ray diffractometry analysis; Scanning electron microscopy; Solid dispersion; Spray drying.
Figures





References
-
- Luger P, Daneck K, Engel W, Trummlitz G, Wagnar K. Structure and physicochemical properties of meloxicam, a new NSAID. Eur J Pharm Sci. 1996;4:175–187. doi: 10.1016/0928-0987(95)00046-1. - DOI
-
- Gupta SK, Bansal P, Bhadwaj RK, Jaiswal J, Velpandian T. Comparison of analgesic and anti-inflammatory activity of meloxicam gel with diclofenac and piroxicam gel in animal models: pharmacokinetic parameters after topical application. Skin Pharmacol Appl Skin Physiol. 2002;15:105–111. doi: 10.1159/000049397. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
