The potential role of interleukin-17 in severe asthma
- PMID: 21773747
- PMCID: PMC4115366
- DOI: 10.1007/s11882-011-0210-y
The potential role of interleukin-17 in severe asthma
Abstract
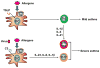
Asthma has long been characterized as a disease of dysregulated T-helper type 2 immune responses to environmental allergens. Clinical studies suggest that asthma is a heterogeneous disorder with distinct types of inflammatory processes. Accumulating evidence suggests that aberrant interleukin (IL)-17 production is a key determinant of severe forms of asthma. However, the identity of IL-17-producing cells and the factors regulating IL-17 production during the course of allergic inflammation remain elusive. In this review, we summarize the potential IL-17-producing cells and their involvement in the inflammatory responses that mediate distinct features of asthma. The role of proinflammatory cytokines and the complement pathway in regulating the generation of IL-17-producing T cells is also discussed. Understanding the biology of IL-17 in the context of allergic inflammation may be informative in the development of novel approaches to the diagnosis and treatment of asthma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicting financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Wills-Karp M. Immunologic basis of antigen-induced airway hyperresponsiveness. Annu Rev Immunol. 1999;17:255–281. - PubMed
-
- Epstein MM. Targeting memory Th2 cells for the treatment of allergic asthma. Pharmacol Ther. 2006;109:107–136. - PubMed
-
- Simpson JL, Scott R, Boyle MJ, Gibson PG. Inflammatory subtypes in asthma: assessment and identification using induced sputum. Respirology. 2006;11:54–61. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

