More than one pathway to action understanding
- PMID: 21775191
- PMCID: PMC3389781
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tics.2011.06.005
More than one pathway to action understanding
Abstract
Many believe that the ability to understand the actions of others is made possible by mirror neurons and a network of brain areas known as the action-observation network (AON). Despite nearly two decades of research into mirror neurons and the AON, however, there is little evidence that they enable the inference of the intention of observed actions. Instead, theories of action selection during action execution indicate that a ventral pathway, linking middle temporal gyrus with the anterior inferior frontal gyrus, might encode these abstract features during action observation. Here I propose that action understanding requires more than merely the AON, and might be achieved through interactions between a ventral pathway and the dorsal AON.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
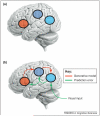

References
-
- Di Pellegrino G, et al. Understanding motor events: a neurophysiological study. Exp. Brain Res. 1992;91:176–180. - PubMed
-
- Gallese V, et al. Action recognition in the premotor cortex. Brain. 1996;119:593–609. - PubMed
-
- Rizzolatti G, et al. Neurophysiological mechanisms underlying the understanding and imitation of action. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2001;2:661–670. - PubMed
-
- Umilta MA, et al. I know what you are doing. A neurophsyiological study. Neuron. 2001;31:155–165. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

