Dopamine acts as a partial agonist for α2A adrenoceptor in melanin-concentrating hormone neurons
- PMID: 21775610
- PMCID: PMC6622637
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6245-10.2011
Dopamine acts as a partial agonist for α2A adrenoceptor in melanin-concentrating hormone neurons
Erratum in
- J Neurosci. 2011 Sep 7;31(36):13023
Abstract
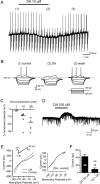
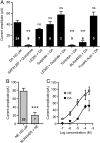
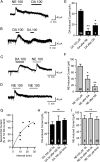
Melanin-concentrating hormone (MCH) is a hypothalamic neuropeptide that promotes positive energy balance and anxiety. Since dopamine (DA) is also closely implicated in these functions, the present study investigated the effect of DA on MCH neurons. Using whole-cell patch-clamp recordings in rat brain slices, we found that DA hyperpolarizes MCH neurons by activating G-protein-activated inwardly rectifying K(+) (GIRK) channels. Pharmacological study indicated that the effect was mediated by α2A adrenoceptors, not DA receptors. DA-induced outward current was also observed in the presence of tetrodotoxin or the dopamine β-hydroxylase inhibitor fusaric acid, suggesting that DA directly binds to α2A receptors on MCH neurons, rather than acting presynaptically or being transformed into norepinephrine (NE) in the slice preparation. The effects of NE and DA were concentration-dependent with EC(50) of 5.9 and 23.7 μm, respectively, and a maximal effect of 106.6 and 57.2 pA, respectively, suggesting that DA functions as a partial agonist. Prolonged (5 min) activation of α2A receptors by either DA or NE attenuated the subsequent response to DA or NE, while 5 s applications were not sufficient to induce desensitization. Therefore, a history of α2A receptor activation by DA or NE can have a lasting inhibitory effect on the catecholaminergic transmission to MCH neurons. Our study suggests that α2A receptors expressed by MCH neurons may be one of the pathways by which DA and NE can interact and modulate mood and energy homeostasis, and this cross talk may have functional implications in mood disorders and obesity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dopamine depresses melanin concentrating hormone neuronal activity through multiple effects on α2-noradrenergic, D1 and D2-like dopaminergic receptors.Neuroscience. 2011 Mar 31;178:89-100. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.01.030. Epub 2011 Jan 22. Neuroscience. 2011. PMID: 21262322
-
Melanin concentrating hormone depresses synaptic activity of glutamate and GABA neurons from rat lateral hypothalamus.J Physiol. 2001 May 15;533(Pt 1):237-52. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2001.0237b.x. J Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11351031 Free PMC article.
-
Dopamine modulates excitability of basolateral amygdala neurons in vitro.J Neurophysiol. 2005 Mar;93(3):1598-610. doi: 10.1152/jn.00843.2004. Epub 2004 Nov 10. J Neurophysiol. 2005. PMID: 15537813
-
The immunoregulatory role of dopamine: an update.Brain Behav Immun. 2010 May;24(4):525-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2009.10.015. Epub 2009 Nov 5. Brain Behav Immun. 2010. PMID: 19896530 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cross interaction of dopaminergic and adrenergic systems in neural modulation.Int J Physiol Pathophysiol Pharmacol. 2014 Oct 11;6(3):137-42. eCollection 2014. Int J Physiol Pathophysiol Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25349636 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Concentration-dependent activation of dopamine receptors differentially modulates GABA release onto orexin neurons.Eur J Neurosci. 2015 Aug;42(3):1976-83. doi: 10.1111/ejn.12967. Epub 2015 Jun 26. Eur J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26036709 Free PMC article.
-
The Melanin-Concentrating Hormone as an Integrative Peptide Driving Motivated Behaviors.Front Syst Neurosci. 2017 May 29;11:32. doi: 10.3389/fnsys.2017.00032. eCollection 2017. Front Syst Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28611599 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Mechanism of α2 adrenoreceptor-dependent Modulation of Neurotransmitter Release at the Neuromuscular Junctions.Neurochem Res. 2024 Feb;49(2):453-465. doi: 10.1007/s11064-023-04052-1. Epub 2023 Oct 28. Neurochem Res. 2024. PMID: 37897557
-
Sleep Deprivation Distinctly Alters Glutamate Transporter 1 Apposition and Excitatory Transmission to Orexin and MCH Neurons.J Neurosci. 2018 Mar 7;38(10):2505-2518. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2179-17.2018. Epub 2018 Feb 5. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29431649 Free PMC article.
-
A Path to Sleep Is through the Eye.eNeuro. 2015 Mar 26;2(2):ENEURO.0069-14.2015. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0069-14.2015. eCollection 2015 Mar-Apr. eNeuro. 2015. PMID: 26464977 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adamson TW, Corll C, Svec F, Porter J. Role of the perifornical hypothalamic monoamine neurotransmitter systems in anorectic effects of endotoxin. Neuroendocrinology. 2010;91:48–55. - PubMed
-
- Aguayo LG, Grossie J. Dopamine inhibits a sustained calcium current through activation of alpha adrenergic receptors and a GTP-binding protein in adult rat sympathetic neurons. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1994;269:503–508. - PubMed
-
- Baldo BA, Daniel RA, Berridge CW, Kelley AE. Overlapping distributions of orexin/hypocretin- and dopamine-beta-hydroxylase immunoreactive fibers in rat brain regions mediating arousal, motivation, and stress. J Comp Neurol. 2003;464:220–237. - PubMed
-
- Bittencourt JC, Presse F, Arias C, Peto C, Vaughan J, Nahon JL, Vale W, Sawchenko PE. The melanin-concentrating hormone system of the rat brain: an immuno- and hybridization histochemical characterization. J Comp Neurol. 1992;319:218–245. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
