The effects of frequent nocturnal home hemodialysis: the Frequent Hemodialysis Network Nocturnal Trial
- PMID: 21775973
- PMCID: PMC3569086
- DOI: 10.1038/ki.2011.213
The effects of frequent nocturnal home hemodialysis: the Frequent Hemodialysis Network Nocturnal Trial
Abstract
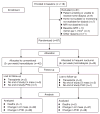
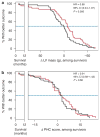
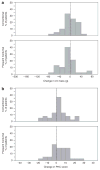
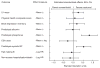
Prior small studies have shown multiple benefits of frequent nocturnal hemodialysis compared to conventional three times per week treatments. To study this further, we randomized 87 patients to three times per week conventional hemodialysis or to nocturnal hemodialysis six times per week, all with single-use high-flux dialyzers. The 45 patients in the frequent nocturnal arm had a 1.82-fold higher mean weekly stdKt/V(urea), a 1.74-fold higher average number of treatments per week, and a 2.45-fold higher average weekly treatment time than the 42 patients in the conventional arm. We did not find a significant effect of nocturnal hemodialysis for either of the two coprimary outcomes (death or left ventricular mass (measured by MRI) with a hazard ratio of 0.68, or of death or RAND Physical Health Composite with a hazard ratio of 0.91). Possible explanations for the left ventricular mass result include limited sample size and patient characteristics. Secondary outcomes included cognitive performance, self-reported depression, laboratory markers of nutrition, mineral metabolism and anemia, blood pressure and rates of hospitalization, and vascular access interventions. Patients in the nocturnal arm had improved control of hyperphosphatemia and hypertension, but no significant benefit among the other main secondary outcomes. There was a trend for increased vascular access events in the nocturnal arm. Thus, we were unable to demonstrate a definitive benefit of more frequent nocturnal hemodialysis for either coprimary outcome.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00271999.
Figures

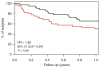
Comment in
-
How best to improve survival in hemodialysis patients: solute clearance or volume control?Kidney Int. 2011 Nov;80(10):1018-20. doi: 10.1038/ki.2011.267. Kidney Int. 2011. PMID: 22042030
-
Benefits of frequent nocturnal home hemodialysis.Kidney Int. 2012 Jul;82(1):114-5; author reply 115. doi: 10.1038/ki.2012.90. Kidney Int. 2012. PMID: 22699382 No abstract available.
References
-
- U.S. Renal Data System, USRDS 2008 Annual Data Report. Atlas of Chronic Kidney Disease and End-Stage Renal Disease in the United States. National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; Bethesda, MD: 2008. http://www.usrds.org. 2009.
-
- Lowrie EG, Laird NM, Parker TF, et al. Effect of the hemodialysis prescription of patient morbidity: report from the National Cooperative Dialysis Study. N Engl J Med. 1981;305:1176–1181. - PubMed
-
- Eknoyan G, Beck GJ, Cheung AK, et al. for the Hemodialysis (HEMO) Study Group. Effect of dialysis dose and membrane flux in maintenance hemodialysis. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:2010–2019. - PubMed
-
- Unruh M, Benz R, Greene T, et al. Effects of hemodialysis dose and membrane flux on health-related quality of life in the HEMO Study. Kidney Int. 2004;66:355–366. - PubMed
-
- Rocco MV, Dwyer JT, Larive B, et al. for the HEMO Study Group. The effect of dialysis dose and membrane flux on nutritional parameters in hemodialysis patients: results of the HEMO Study. Kidney Int. 2004;65:2321–2334. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

