Long-lasting effects of undernutrition
- PMID: 21776204
- PMCID: PMC3137999
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph8061817
Long-lasting effects of undernutrition
Abstract
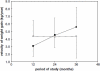
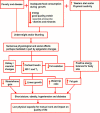
Undernutrition is one of the most important public health problems, affecting more than 900 million individuals around the World. It is responsible for the highest mortality rate in children and has long-lasting physiologic effects, including an increased susceptibility to fat accumulation mostly in the central region of the body, lower fat oxidation, lower resting and postprandial energy expenditure, insulin resistance in adulthood, hypertension, dyslipidaemia and a reduced capacity for manual work, among other impairments. Marked changes in the function of the autonomic nervous system have been described in undernourished experimental animals. Some of these effects seem to be epigenetic, passing on to the next generation. Undernutrition in children has been linked to poor mental development and school achievement as well as behavioural abnormalities. However, there is still a debate in the literature regarding whether some of these effects are permanent or reversible. Stunted children who had experienced catch-up growth had verbal vocabulary and quantitative test scores that did not differ from children who were not stunted. Children treated before 6 years of age in day-hospitals and who recovered in weight and height have normal body compositions, bone mineral densities and insulin production and sensitivity.
Keywords: body composition; dyslipidaemia; energy expenditure; hypertension; insulin; undernutrition.
Figures

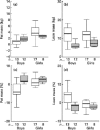
 ) and nonstunted children (□) (overall group) between the two study visits. (a) fat mass; (b) lean mass; (c) fat mass percentage; (d) lean mass percentage. The boxes represent the interquartile ranges, which contain 50% of values; the whiskers are the highest and lowest values (excluding outliers), and the line across each box indicates the median. Reprinted with permission from Brit. J. Nutr. [26].
) and nonstunted children (□) (overall group) between the two study visits. (a) fat mass; (b) lean mass; (c) fat mass percentage; (d) lean mass percentage. The boxes represent the interquartile ranges, which contain 50% of values; the whiskers are the highest and lowest values (excluding outliers), and the line across each box indicates the median. Reprinted with permission from Brit. J. Nutr. [26].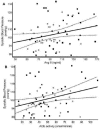
References
-
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. The State of Food Insecurity in the World - Addressing Food Insecurity in Protracted Crises. FAO; Rome, Italy: 2010.
-
- Black RE, Allen LH, Bhutta ZA, Caulfield LE, de Onis M, Ezzati M, Mathers C, Rivera J. Maternal and child undernutrition: global and regional exposures and health consequences. Lancet. 2008;371:243–260. - PubMed
-
- Repositioning Nutrition as Central to Development A Strategy for Large-Scale Action. The World Bank; Washington, DC, USA: 2006. Available online: http://siteresources.worldbank.org/NUTRITION/Resources/281846-1131636806... (accessed on 13 September 2010)
-
- Kalhan SC, Prentice AM, Yajnik CS, editors. Emerging Societies—Coexistence of Childhood Malnutrition and Obesity. Vol. 63. Nestlé Nutrition Institute; Vevey, Switzerland: 2009. pp. I–XI.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

