Translational connection of TGFβ signaling: Phosphorylation of eEF1A1 by TβR-I inhibits protein synthesis
- PMID: 21776411
- PMCID: PMC3136913
- DOI: 10.4161/sgtp.2.2.15603
Translational connection of TGFβ signaling: Phosphorylation of eEF1A1 by TβR-I inhibits protein synthesis
Abstract
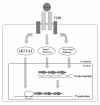
Transforming growth factor-β (TGFβ) signaling pathways regulate a wide array of cellular activities that are crucial for cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration and differentiation. TGFβ signaling pathways are initiated by ligand-activated TGFβ receptors, with type I TGFβ receptors (TβR-I) kinase being essential for phosphorylation of downstream targets. Until now, a prevalent view was that the TGFβ intracellular signaling targets would regulate transcription. Recently, we uncovered a novel TGFβ signaling pathway that exerts a direct regulatory effect on mRNA translation and protein synthesis. Eukaryotic elongation factor eEF1A1 is a GTP-binding protein that plays a central role in protein synthesis. By using a screening method for kinase substrate that was developed in our laboratory, we identified eEF1A1 as a novel substrate of TβR-I. This shed a new light on the convergence of TGFβ signaling and protein synthesis. We also showed phosphorylation of eEF1A1 at Ser300 by TβR-I prevents aa-tRNA binding to eEF1A1. As a consequence, TGFβ-dependent phosphorylation of eEF1A1 has an inhibitory effect on protein synthesis and cell proliferation. Therefore, we unveiled a novel regulatory mechanism of cellular proliferation by TGFβ at the translational level. Here we discuss this finding in the context of its potential role in the multiplicity of TGFβ signaling, and in the regulation of fundamental cellular functions, such as proliferation.
Figures

References
-
- Knudsen SM, Frydenberg J, Clark BF, Leffers H. Tissue-dependent variation in the expression of elongation factor-1 alpha isoforms: isolation and characterisation of a cDNA encoding a novel variant of human elongation-factor 1alpha. Eur J Biochem. 1993;215:549–554. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb18064.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lee S, Francoeur AM, Liu S, Wang E. Tissue-specific expression in mammalian brain, heart and muscle of S1, a member of the elongation factor-1alpha gene family. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:24064–24068. - PubMed
-
- Kato MV, Sato H, Nagayoshi M, Ikawa Y. Upregulation of the elongation factor-1alpha gene by p53 in association with death of an erythroleukemic cell line. Blood. 1997;90:1373–1378. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
