Dissecting the functions of conserved prolines within transmembrane helices of the D2 dopamine receptor
- PMID: 21776983
- PMCID: PMC3199346
- DOI: 10.1021/cb200153g
Dissecting the functions of conserved prolines within transmembrane helices of the D2 dopamine receptor
Abstract
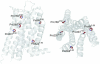
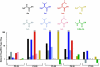
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) contain a number of conserved proline residues in their transmembrane helices, and it is generally assumed these play important functional and/or structural roles. Here we use unnatural amino acid mutagenesis, employing α-hydroxy acids and proline analogues, to examine the functional roles of five proline residues in the transmembrane helices of the D2 dopamine receptor. The well-known tendency of proline to disrupt helical structure is important at all sites, while we find no evidence for a functional role for backbone amide cis-trans isomerization, another feature associated with proline. At most proline sites, the loss of the backbone NH is sufficient to explain the role of the proline. However, at one site, P210(5.50), a substituent on the backbone N appears to be essential for proper function. Interestingly, the pattern in functional consequences that we see is mirrored in the pattern of structural distortions seen in recent GPCR crystal structures.
Figures

References
-
- Barlow DJ, Thornton JM. Helix geometry in proteins. J Mol Biol. 1988;201:601–619. - PubMed
-
- Woolfson DN, Williams DH. The influence of proline residues on alpha-helical structure. FEBS Lett. 1990;277:185–188. - PubMed
-
- Reiersen H, Rees AR. The hunchback and its neighbours: proline as an environmental modulator. Trends Biochem Sci. 2001;26:679–684. - PubMed
-
- Cordes FS, Bright JN, Sansom MS. Proline-induced distortions of transmembrane helices. J Mol Biol. 2002;323:951–960. - PubMed
-
- Dugave C, Demange L. Cis-trans isomerization of organic molecules and biomolecules: implications and applications. Chem Rev. 2003;103:2475–2532. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

