Role of tissue transglutaminase 2 in the acquisition of a mesenchymal-like phenotype in highly invasive A431 tumor cells
- PMID: 21777419
- PMCID: PMC3150327
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-4598-10-87
Role of tissue transglutaminase 2 in the acquisition of a mesenchymal-like phenotype in highly invasive A431 tumor cells
Abstract
Background: Cancer progression is closely linked to the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) process. Studies have shown that there is increased expression of tissue tranglutaminase (TG2) in advanced invasive cancer cells. TG2 catalyzes the covalent cross-linking of proteins, exhibits G protein activity, and has been implicated in the modulation of cell adhesion, migration, invasion and cancer metastasis. This study explores the molecular mechanisms associated with TG2's involvement in the acquisition of the mesenchymal phenotype using the highly invasive A431-III subline and its parental A431-P cells.
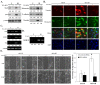
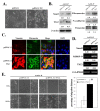
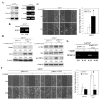
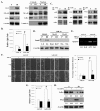
Results: The A431-III tumor subline displays increased expression of TG2. This is accompanied by enhanced expression of the mesenchymal phenotype, and this expression is reversed by knockdown of endogenous TG2. Consistent with this, overexpression of TG2 in A431-P cells advanced the EMT process. Furthermore, TG2 induced the PI3K/Akt activation and GSK3β inactivation in A431 tumor cells and this increased Snail and MMP-9 expression resulting in higher cell motility. TG2 also upregulated NF-κB activity, which also enhanced Snail and MMP-9 expression resulting in greater cell motility; interestingly, this was associated with the formation of a TG2/NF-κB complex. TG2 facilitated acquisition of a mesenchymal phenotype, which was reversed by inhibitors of PI3K, GSK3 and NF-κB.
Conclusions: This study reveals that TG2 acts, at least in part, through activation of the PI3K/Akt and NF-κB signaling systems, which then induce the key mediators Snail and MMP-9 that facilitate the attainment of a mesenchymal phenotype. These findings support the possibility that TG2 is a promising target for cancer therapy.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Up-regulation of fibronectin and tissue transglutaminase promotes cell invasion involving increased association with integrin and MMP expression in A431 cells.Anticancer Res. 2010 Oct;30(10):4177-86. Anticancer Res. 2010. PMID: 21036738
-
Evidence that GTP-binding domain but not catalytic domain of transglutaminase 2 is essential for epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in mammary epithelial cells.Breast Cancer Res. 2012 Jan 6;14(1):R4. doi: 10.1186/bcr3085. Breast Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22225906 Free PMC article.
-
Matrix metalloproteinase-9 cooperates with transcription factor Snail to induce epithelial-mesenchymal transition.Cancer Sci. 2011 Apr;102(4):815-27. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2011.01861.x. Epub 2011 Feb 9. Cancer Sci. 2011. PMID: 21219539
-
Tissue transglutaminase as a central mediator in inflammation-induced progression of breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res. 2013 Feb 25;15(1):202. doi: 10.1186/bcr3371. Breast Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23673317 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tissue transglutaminase-mediated chemoresistance in cancer cells.Drug Resist Updat. 2007 Aug-Oct;10(4-5):144-51. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2007.06.002. Epub 2007 Jul 27. Drug Resist Updat. 2007. PMID: 17662645 Review.
Cited by
-
Elucidating the mechanism of action of alpha-1-antitrypsin using retinal pigment epithelium cells exposed to high glucose. Potential use in diabetic retinopathy.PLoS One. 2020 Feb 7;15(2):e0228895. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0228895. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32032388 Free PMC article.
-
Co-Expression of Adaptor Protein FAM159B with Different Markers for Neuroendocrine Cells: An Immunocytochemical and Immunohistochemical Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 4;23(21):13503. doi: 10.3390/ijms232113503. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36362289 Free PMC article.
-
The Role and Mechanism of Transglutaminase 2 in Regulating Hippocampal Neurogenesis after Traumatic Brain Injury.Cells. 2023 Feb 9;12(4):558. doi: 10.3390/cells12040558. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36831225 Free PMC article.
-
Transglutaminase 2 takes center stage as a cancer cell survival factor and therapy target.Mol Carcinog. 2019 Jun;58(6):837-853. doi: 10.1002/mc.22986. Epub 2019 Mar 28. Mol Carcinog. 2019. PMID: 30693974 Free PMC article.
-
NF-κB in biology and targeted therapy: new insights and translational implications.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024 Mar 4;9(1):53. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01757-9. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024. PMID: 38433280 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

