Assessment of severity and frequency of self-reported hypoglycemia on quality of life in patients with type 2 diabetes treated with oral antihyperglycemic agents: A survey study
- PMID: 21777428
- PMCID: PMC3148563
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-0500-4-251
Assessment of severity and frequency of self-reported hypoglycemia on quality of life in patients with type 2 diabetes treated with oral antihyperglycemic agents: A survey study
Abstract
Background: Some oral antihyperglycemic agents may increase risk of hypoglycemia and thereby reduce patient quality of life. Our objective was to assess the impact of the severity and frequency of self-reported hypoglycemia on health-related quality of life (HRQoL) among patients with type 2 diabetes treated with oral antihyperglycemic agents.
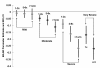
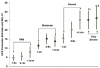
Findings: A follow-up survey was conducted in participants with self-reported type 2 diabetes treated with oral antihyperglycemic agents from the US National Health and Wellness Survey 2007. Data were collected on the severity and frequency of hypoglycemic episodes in the 6 months prior to the survey, with severity defined as mild (no interruption of activities), moderate (some interruption of activities), severe (needed assistance of others), or very severe (needed medical attention). HRQoL was assessed using the EuroQol-5D Questionnaire (EQ-5D) US weighted summary score (utility) and Worry subscale of the Hypoglycemia Fear Survey (HFS). Of the participants who completed the survey (N = 1,984), mean age was 58 years, 57% were male, 72% reported an HbA1c <7.0%, and 50% reported treatment with a sulfonylurea-containing regimen. Hypoglycemic episodes were reported by 63% of patients (46% mild, 37% moderate, 13% severe and 4% very severe). For patients reporting hypoglycemia, mean utility score was significantly lower (0.78 versus 0.86, p < 0.0001) and mean HFS score was significantly higher (17.5 versus 6.2, p < 0.0001) compared to patients not reporting hypoglycemia. Differences in mean scores between those with and without hypoglycemia increased with the level of severity (mild, moderate, severe, very severe) for utility (0.03, 0.09, 0.18, 0.23) and HFS (6.1, 13.9, 20.1, 25.6), respectively. After adjusting for age, gender, weight gain, HbA1c, microvascular complications, and selected cardiovascular conditions, the utility decrement was 0.045 (by level of severity: 0.009, 0.055, 0.131, 0.208), and the HFS increase was 9.6 (by severity: 5.3, 12.4, 17.6, 23.2). HRQoL further decreased with greater frequency of hypoglycemic episodes.
Conclusions: Self-reported hypoglycemia is independently associated with lower HRQoL, and the magnitude of this reduction increases with both severity and frequency of episodes in patients with type 2 diabetes treated with oral antihyperglycemic agents.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hypoglycemia is associated with increased worry and lower quality of life among patients with type 2 diabetes treated with oral antihyperglycemic agents in the Asia-Pacific region.Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2012 May;96(2):141-8. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2011.12.027. Epub 2012 Jan 21. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2012. PMID: 22265956
-
Impact of Hypoglycemia on Health-Related Quality of Life among Type 2 Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Study in Thailand.J Diabetes Res. 2019 Oct 23;2019:5903820. doi: 10.1155/2019/5903820. eCollection 2019. J Diabetes Res. 2019. PMID: 31772942 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoglycaemia in patients with type 2 diabetes treated with a combination of metformin and sulphonylurea therapy in France.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2008 Jun;10 Suppl 1:16-24. doi: 10.1111/j.1463-1326.2008.00883.x. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2008. PMID: 18435670
-
WHICH FACTORS MAY AFFECT THE QUALITY OF LIFE IN PATIENTS WITH TYPE 1 DIABETES MELLITUS USING THE MEDTRONIC VEO CONTINUOUS SUBCUTANEOUS INSULIN INFUSION PUMP?Georgian Med News. 2018 Apr;(277):61-67. Georgian Med News. 2018. PMID: 29745917
-
Is hypoglycemia fear independently associated with health-related quality of life?Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2014 Nov 30;12:167. doi: 10.1186/s12955-014-0167-3. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2014. PMID: 25433668 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Cost-Effectiveness of Dapagliflozin versus Acarbose as a Monotherapy in Type 2 Diabetes in China.PLoS One. 2016 Nov 2;11(11):e0165629. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0165629. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27806087 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-effectiveness Analysis of a Flash Glucose Monitoring System for Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Receiving Intensive Insulin Treatment in Sweden.Eur Endocrinol. 2018 Sep;14(2):73-79. doi: 10.17925/EE.2018.14.2.73. Epub 2018 Sep 10. Eur Endocrinol. 2018. PMID: 30349598 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Documentation of hypoglycemia assessment among adults with diabetes during clinical encounters in primary care and endocrinology practices.Endocrine. 2020 Mar;67(3):552-560. doi: 10.1007/s12020-019-02147-w. Epub 2019 Dec 4. Endocrine. 2020. PMID: 31802353 Free PMC article.
-
Health state utility values ranges across varying stages and severity of type 2 diabetes-related complications: A systematic review.PLoS One. 2024 Apr 4;19(4):e0297589. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0297589. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38574169 Free PMC article.
-
The influence of hypoglycemia on the specific quality of life in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a comparative cross-sectional study of diabetics with and without hypoglycemia in Xi'an, China.Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2021 May 19;19(1):151. doi: 10.1186/s12955-021-01790-0. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2021. PMID: 34011369 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Turner R, Holman R, Cull C, Stratton I, Matthews D, Frighi V. Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33) Lancet. 1998;352:837–853. - PubMed
-
- Cryer PE, Childs PB. Negotiating the barrier of hypoglycemia in diabetes. Diabetes Spectr. 2002;15:20–27. doi: 10.2337/diaspect.15.1.20. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

