Chemotaxis in cancer
- PMID: 21779009
- PMCID: PMC4030706
- DOI: 10.1038/nrc3078
Chemotaxis in cancer
Abstract
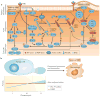
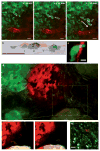
Chemotaxis of tumour cells and stromal cells in the surrounding microenvironment is an essential component of tumour dissemination during progression and metastasis. This Review summarizes how chemotaxis directs the different behaviours of tumour cells and stromal cells in vivo, how molecular pathways regulate chemotaxis in tumour cells and how chemotaxis choreographs cell behaviour to shape the tumour microenvironment and to determine metastatic spread. The central importance of chemotaxis in cancer progression is highlighted by discussion of the use of chemotaxis as a prognostic marker, a treatment end point and a target of therapeutic intervention.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare competing financial interests: see Web version for details.
Figures


References
-
- Condeelis J, Singer RH, Segall JE. The great escape: when cancer cells hijack the genes for chemotaxis and motility. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2005;21:695–718. - PubMed
-
- Farrow B, Albo D, Berger DH. The role of the tumor microenvironment in the progression of pancreatic cancer. J Surg Res. 2008;149:319–328. - PubMed
-
- Condeelis J, Segall JE. Intravital imaging of cell movement in tumours. Nature Rev Cancer. 2003;3:921–930. - PubMed
-
- Roussos ET, et al. Mena invasive (MenaINV) promotes multicellular streaming motility and transendothelial migration in a mouse model of breast cancer. J Cell Sci. 2011;124:2120–2131. This study demonstrates how a MENA invasion-specific isoform promotes multicellular streaming in vivo in mouse models of breast cancer. This was the first study to define multicellular streaming migration of breast tumour cells in vivo by intravital imaging. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

