Emerging Roles for SSeCKS/Gravin/AKAP12 in the Control of Cell Proliferation, Cancer Malignancy, and Barriergenesis
- PMID: 21779438
- PMCID: PMC3092279
- DOI: 10.1177/1947601910392984
Emerging Roles for SSeCKS/Gravin/AKAP12 in the Control of Cell Proliferation, Cancer Malignancy, and Barriergenesis
Abstract
Emerging data suggest that SSeCKS/Gravin/AKAP12 ("AKAP12"), originally identified as an autoantigen in cases of myasthenia gravis, controls multiple biological processes through its ability to scaffold key signaling proteins such as protein kinase (PK) C and A, calmodulin, cyclins, phosphoinositides, "long" β-1,4 galactosyltransferase (GalTase) isoform, Src, as well as the actin cytoskeleton in a spatiotemporal manner. Specialized functions attributed to AKAP12 include the suppression of cancer malignancy, especially aspects of metastatic progression, regulation of blood-brain and blood-retina barrier formation, and resensitization of β2-adrenergic pain receptors. Recent data identify a direct role for AKAP12 in cytokinesis completion, further suggesting a function as a negative regulator of cell senescence. The current review will discuss the emerging knowledge base of AKAP12-related biological roles and how the factors that affect AKAP12 expression or that interact with AKAP12 at the protein level control cancer progression and blood-tissue barrier formation.
Keywords: G1→S progression; PKA; PKC; Ras; SSeCKS/Gravin/AKAP12; Src; VEGF; cell motility; cell-cell barriers; cyclin D; cytokinesis; metastasis; neovascularization; prostate cancer; tumor invasiveness.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the authorship and/or publication of this article.
Figures
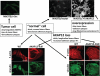

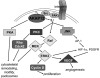
References
-
- Ln X, Tombler E, Nelson PJ, Ross M, Gelman IH. A novel src- and ras-suppressed protein kinase C substrate associated with cytoskeletal architecture. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:28, 430,-28, 438 - PubMed
-
- Chapline C, Cottom J, Tobin H, Hulmes J, Crabb J, Jaken S. A major, transformation-sensitive PKC-binding protein is also a PKC substrate involved in cytoskeletal remodeling. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:19482-9 - PubMed
-
- Lin X, Gelman IH. Re-expression of the major protein kinase C substrate, SSeCKS, suppresses v-src-induced morphological transformation and tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 1997;57:2304-12 - PubMed
-
- Xia W, Gelman IH. Mitogen- and FAK-regulated tyrosine phosphorylation of the SSeCKS scaffolding protein modulates its actin-binding properties. Exp Cell Res. 2002;277:139-51 - PubMed
-
- Tao J, Wang HY, Malbon C. Src docks to AKAP Gravin, regulating beta-adrenergic receptor resensitization and recycling. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:6597-608 - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
