The Putative PAX8/PPARγ Fusion Oncoprotein Exhibits Partial Tumor Suppressor Activity through Up-Regulation of Micro-RNA-122 and Dominant-Negative PPARγ Activity
- PMID: 21779480
- PMCID: PMC3111009
- DOI: 10.1177/1947601911405045
The Putative PAX8/PPARγ Fusion Oncoprotein Exhibits Partial Tumor Suppressor Activity through Up-Regulation of Micro-RNA-122 and Dominant-Negative PPARγ Activity
Abstract
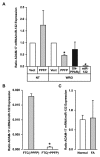
In vitro studies have demonstrated that the PAX8/PPARγ fusion protein (PPFP), which occurs frequently in follicular thyroid carcinomas (FTC), exhibits oncogenic activity. However, paradoxically, a meta-analysis of extant tumor outcome studies indicates that 68% of FTC-expressing PPFP are minimally invasive compared to only 32% of those lacking PPFP (χ(2) = 6.86, P = 0.008), suggesting that PPFP favorably impacts FTC outcomes. In studies designed to distinguish benign thyroid neoplasms from thyroid carcinomas, the previously identified tumor suppressor miR-122, a major liver micro-RNA (miR) that is decreased in hepatocellular carcinoma, was increased 8.9-fold (P < 0.05) in all FTC versus normal, 9.2-fold in FTC versus FA (P < 0.05), and 16.8-fold (P < 0.001) in FTC + PPFP versus FTC - PPFP. Constitutive expression of PPFP in the FTC-derived cell line WRO (WRO-PPFP) caused a 5-fold increase of miR-122 expression (P < 0.05) and a striking 5.1-fold reduction (P < 0.0001) in tumor progression compared to WRO-vector cells in a mouse xenograft model. Constitutive expression of either miR-122 or a dominant-negative PPARγ mutant in WRO cells was less effective than PPFP at inhibiting xenograft tumor progression (1.8-fold [P < 0.001] and 1.7-fold [P < 0.03], respectively). PPFP-induced up-regulation of miR-122 expression was independent of its known dominant-negative PPARγ activity. Up-regulation of miR-122 negatively regulates ADAM-17, a known downstream target, in thyroid cells, suggesting an antiangiogenic mechanism in thyroid carcinoma. This latter inference is directly supported by reduced CD-31 expression in WRO xenografts expressing PPFP, miR-122, and DN-PPARγ. We conclude that, in addition to its apparent oncogenic potential in vitro, PPFP exhibits paradoxical tumor suppressor activity in vivo, mediated by multiple mechanisms including up-regulation of miR-122 and dominant-negative inhibition of PPARγ activity.
Keywords: PAX8/PPARγ; follicular thyroid carcinoma; fusion protein; miR-122; tumor suppressor.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the authorship and/or publication of this article.
Figures





References
-
- Farahati J, Geling M, Mader U, et al. Changing trends of incidence and prognosis of thyroid carcinoma in lower Franconia, Germany, from 1981-1995. Thyroid. 2004;14:141-7 - PubMed
-
- Nambiar M, Kari V, Raghavan SC. Chromosomal translocations in cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008;1786:139-52 - PubMed
-
- Gregory Powell J, Wang X, Allard BL, et al. The PAX8/PPARgamma fusion oncoprotein transforms immortalized human thyrocytes through a mechanism probably involving wild-type PPARgamma inhibition. Oncogene. 2004;23:3634-41 - PubMed
-
- Au AY, McBride C, Wilhelm KG, Jr., et al. PAX8-peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma) disrupts normal PAX8 or PPARgamma transcriptional function and stimulates follicular thyroid cell growth. Endocrinology. 2006;147:367-76 - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
