Enhanced delivery of mda-7/IL-24 using a serotype chimeric adenovirus (Ad.5/3) in combination with the Apogossypol derivative BI-97C1 (Sabutoclax) improves therapeutic efficacy in low CAR colorectal cancer cells
- PMID: 21780116
- PMCID: PMC3228880
- DOI: 10.1002/jcp.22947
Enhanced delivery of mda-7/IL-24 using a serotype chimeric adenovirus (Ad.5/3) in combination with the Apogossypol derivative BI-97C1 (Sabutoclax) improves therapeutic efficacy in low CAR colorectal cancer cells
Abstract
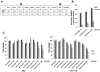
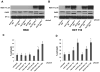
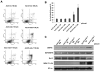
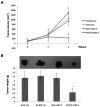
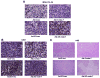
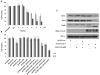
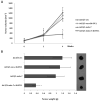
Adenovirus (Ad)-based gene therapy represents a potentially viable strategy for treating colorectal cancer. The infectivity of serotype 5 adenovirus (Ad.5), routinely used as a transgene delivery vector, is dependent on Coxsackie-adenovirus receptors (CAR). CAR expression is downregulated in many cancers thus preventing optimum therapeutic efficiency of Ad.5-based therapies. To overcome the low CAR problem, a serotype chimerism approach was used to generate a recombinant Ad (Ad.5/3) that is capable of infecting cancer cells via Ad.3 receptors in a CAR-independent manner. We evaluated the improved transgene delivery and efficacy of Ad.5/3 recombinant virus expressing melanoma differentiation associated gene-7/interleukin-24 (mda-7/IL-24), an effective wide-spectrum cancer-selective therapeutic. In low CAR human colorectal cancer cells RKO, wild-type Ad.5 virus expressing mda-7/IL-24 (Ad.5-mda-7) failed to infect efficiently resulting in lack of expression of MDA-7/IL-24 or induction of apoptosis. However, a recombinant Ad.5/3 virus expressing mda-7/IL-24 (Ad.5/3-mda-7) efficiently infected RKO cells resulting in higher MDA-7/IL-24 expression and inhibition of cell growth both in vitro and in nude mice xenograft models. Addition of the novel Bcl-2 family pharmacological inhibitor Apogossypol derivative BI-97C1 (Sabutoclax) significantly augmented the efficacy of Ad.5/3-mda-7. A combination regimen of suboptimal doses of Ad.5/3-mda-7 and BI-97C1 profoundly enhanced cytotoxicity in RKO cells both in vitro and in vivo. Considering the fact that Ad.5-mda-7 has demonstrated significant objective responses in a Phase I clinical trial for advanced solid tumors, Ad.5/3-mda-7 alone or in combination with BI-97C1 would be predicted to exert significantly improved therapeutic efficacy in colorectal cancer patients.
Copyright © 2011 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Fong Y, Kemeny N, Paty P, Blumgart LH, Cohen AM. Treatment of colorectal cancer: hepatic metastasis. Semin Surg Oncol. 1996;12(4):219–252. - PubMed
-
- Lynch HT, de la Chapelle A. Hereditary colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2003;348(10):919–932. in eng. - PubMed
-
- Chu RL, Post DE, Khuri FR, Van Meir EG. Use of replicating oncolytic adenoviruses in combination therapy for cancer. Clinical Cancer Res. 2004;10(16):5299–5312. - PubMed
-
- Reid T, et al. Hepatic arterial infusion of a replication-selective oncolytic adenovirus (dl1520): phase II viral, immunologic, and clinical endpoints. Cancer Res. 2002;62(21):6070–6079. - PubMed
-
- Korn WM, et al. Expression of the coxsackievirus- and adenovirus receptor in gastrointestinal cancer correlates with tumor differentiation. Cancer Gene Ther. 2006;13(8):792–797. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

