Errorless and errorful learning modulated by transcranial direct current stimulation
- PMID: 21781298
- PMCID: PMC3154153
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2202-12-72
Errorless and errorful learning modulated by transcranial direct current stimulation
Abstract
Background: Errorless learning is advantageous over trial and error learning (errorful learning) as errors are avoided during learning resulting in increased memory performance. Errorful learning challenges the executive control system of memory processes as the erroneous items compete with the correct items during retrieval. The left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC) is a core region involved in this executive control system. Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) can modify the excitability of underlying brain functioning.
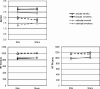
Results: In a single blinded tDCS study one group of young healthy participants received anodal and another group cathodal tDCS of the left DLPFC each compared to sham stimulation. Participants had to learn words in an errorless and an errorful manner using a word stem completion paradigm. The results showed that errorless compared to errorful learning had a profound effect on the memory performance in terms of quality. Anodal stimulation of the left DLPFC did not modulate the memory performance following errorless or errorful learning. By contrast, cathodal stimulation hampered memory performance after errorful learning compared to sham, whereas there was no modulation after errorless learning.
Conclusions: Concluding, the study further supports the advantages of errorless learning over errorful learning. Moreover, cathodal stimulation of the left DLPFC hampered memory performance following the conflict-inducing errorful learning as compared to no modulation after errorless learning emphasizing the importance of the left DLPFC in executive control of memory.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Recognition of face-name associations after errorless and errorful learning: an fMRI study.BMC Neurosci. 2013 Mar 13;14:30. doi: 10.1186/1471-2202-14-30. BMC Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23496800 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of cortical responses by transcranial direct current stimulation of dorsolateral prefrontal cortex: A resting-state EEG and TMS-EEG study.Brain Stimul. 2018 Sep-Oct;11(5):1024-1032. doi: 10.1016/j.brs.2018.06.004. Epub 2018 Jun 18. Brain Stimul. 2018. PMID: 29921529 Clinical Trial.
-
Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) of the left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex modulates declarative memory.Brain Stimul. 2012 Jul;5(3):231-241. doi: 10.1016/j.brs.2011.06.007. Epub 2011 Jul 26. Brain Stimul. 2012. PMID: 21840287
-
Prefrontal but not cerebellar tDCS attenuates renewal of extinguished conditioned eyeblink responses.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2020 Apr;170:107137. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2019.107137. Epub 2019 Dec 12. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2020. PMID: 31838223 Review.
-
Errorless learning in cognitive rehabilitation: a critical review.Neuropsychol Rehabil. 2012;22(2):138-68. doi: 10.1080/09602011.2011.639619. Epub 2012 Jan 16. Neuropsychol Rehabil. 2012. PMID: 22247957 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Modulating Memory Performance in Healthy Subjects with Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation Over the Right Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex.PLoS One. 2015 Dec 17;10(12):e0144838. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0144838. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26679936 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Role of BDNF Signaling in Memory Enhancement Induced by Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation.Front Neurosci. 2018 Jun 26;12:427. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00427. eCollection 2018. Front Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29997473 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation of the Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex Modulates Cognitive Function Related to Motor Execution During Sequential Task: A Randomized Control Study.Front Hum Neurosci. 2022 Jun 14;16:890963. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2022.890963. eCollection 2022. Front Hum Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35774483 Free PMC article.
-
Errorful and errorless learning: The impact of cue-target constraint in learning from errors.Mem Cognit. 2014 Aug;42(6):898-911. doi: 10.3758/s13421-014-0408-z. Mem Cognit. 2014. PMID: 24615717
-
The effect of the interval-between-sessions on prefrontal transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) on cognitive outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2016 Oct;123(10):1159-72. doi: 10.1007/s00702-016-1558-x. Epub 2016 May 4. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2016. PMID: 27145765
References
-
- Deese J. On the prediction of occurrence of particular verbal intrusions in immediate recall. J Exp Psychol. 1959;58(1):17–22. - PubMed
-
- Roediger HL, McDermott KB. Creating False Memories: Remembering Words not Presented in Lists. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition. 1995;21(4):803–814.
-
- Brainerd CJ, Reyna VF. Fuzzy-trace theory: dual processes in memory, reasoning, and cognitive neuroscience. Adv Child Dev Behav. 2001;28:41–100. - PubMed
-
- Reynolds JR, McDermott KB, Braver TS. A direct comparison of anterior prefrontal cortex involvement in episodic retrieval and integration. Cereb Cortex. 2006;16(4):519–528. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources