Phage display identifies two Caprine Arthritis Encephalitis Virus env epitopes
- PMID: 21781322
- PMCID: PMC3162499
- DOI: 10.1186/1297-9716-42-87
Phage display identifies two Caprine Arthritis Encephalitis Virus env epitopes
Abstract
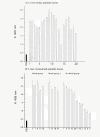
Using phage display and IgG of a goat infected with Caprine Arthritis Encephalitis Virus (CAEV) we obtained families of 7 mer constrained peptides with consensus motifs LxSDPF/Y and SWN/KHWSY and mapped the epitopes mimicked by them at the Env 6-LISDPY-11 and 67-WNTYHW-72 sites of the mature gp135 amino acid sequence. The first epitope fell into the N-terminal immunogenic aa1-EDYTLISDPYGFS- aa14 site identified previously with a synthetic peptide approach; the second epitope has not been described previously. The first epitope is mostly conserved across CAEV isolates whereas the second newly described epitope is extremely conserved in Small Ruminant Lentiviruses env sequences. As being immunodominant, the epitopes are candidate targets for mimotope-mediated diagnosis and/or neutralization.
Figures

Similar articles
-
B-cell epitopes of the envelope glycoprotein of caprine arthritis-encephalitis virus and antibody response in infected goats.J Gen Virol. 2000 Dec;81(Pt 12):2929-2940. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-81-12-2929. J Gen Virol. 2000. PMID: 11086124
-
Caprine arthritis-encephalitis virus envelope surface glycoprotein regions interacting with the transmembrane glycoprotein: structural and functional parallels with human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp120.J Virol. 2003 Nov;77(21):11578-87. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.21.11578-11587.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 14557643 Free PMC article.
-
Antibody reactivity to the immunodominant epitopes of the caprine arthritis-encephalitis virus gp38 transmembrane protein associates with the development of arthritis.J Virol. 1994 Nov;68(11):7139-47. doi: 10.1128/JVI.68.11.7139-7147.1994. J Virol. 1994. PMID: 7933096 Free PMC article.
-
Recombinant gp135 envelope glycoproteins of caprine arthritis-encephalitis lentivirus variants inhibit homologous and heterologous variant-specific neutralizing antibodies.Virology. 1991 Nov;185(1):2-9. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90747-y. Virology. 1991. PMID: 1718084
-
Variability and immunogenicity of caprine arthritis-encephalitis virus surface glycoprotein.J Virol. 2000 Jul;74(13):6178-85. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.13.6178-6185.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 10846103 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pepin M, Vitu C, Russo P, Mornex JF, Peterhans E. Maedi-visna virus infection in sheep: a review. Vet Res. 1998;29:341–367. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

