To be at the right place at the right time
- PMID: 21781323
- PMCID: PMC3154858
- DOI: 10.1186/1746-1596-6-68
To be at the right place at the right time
Abstract
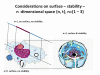
Aim: To analyze the hypothesis of events or neighborhood interactions that is based upon recognizable structures of systems which possess a surface in a four dimensional space-time constellation {x, y, z, t}. To include the theory of hierarchic order of structures and aspects of thermodynamically open systems, especially entropy, structural entropy and entropy flow.
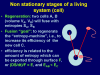
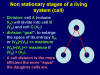
Hypothesis: Any structure is a space-time constellation that occupies a unique space in its environment. The environment can be a system too, and is assumed to be (nearly) constant. Structures can interact in their environment and create a new structure at a higher order level. Interacting structures that create a surface are called a system. Starting from the bottom, such a system is characterized by its inner structures, its surface function, and its neighborhood. Interaction with a neighboring system is called an event. An event can alter a system, create new systems or induce the decay of a system, dependent upon the surrounding lower level system (background).
Results: The hypothesis results in a uniform theory about matter, life, diseases, or behavior. Concrete applications permit the estimation of duration of life in man, for example the effect of solid cancer in man, or appearance of protozoans in sexual or asexual reduplication. In addition, it can successfully describe the development of the universe (small exceed of matter above antimatter at the big bang), or the increase of structures (and systems) with increasing time (development of intelligent systems). The three dimensional space possesses the lowest number of mandatory dimensions to implement such a system.
Figures
Similar articles
-
BIROpen: open access meets flexibility.Br J Radiol. 2013 Apr;86(1024):20130116. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20130116. Epub 2013 Feb 28. Br J Radiol. 2013. PMID: 23449439 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The Open Access issue revisited.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2007 Oct;189(4):753-4. doi: 10.2214/AJR.07.6624. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2007. PMID: 17886401 No abstract available.
-
The Electronic Era: Unintended Consequences?AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2016 Jan;206(1):1-2. doi: 10.2214/AJR.15.15725. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2016. PMID: 26700330 No abstract available.
-
The application of thermodynamic principles to histochemical and morphometric tissue research: principles and practical outline with focus on the glycosciences.Cell Tissue Res. 1999 Jun;296(3):443-55. doi: 10.1007/s004410051305. Cell Tissue Res. 1999. PMID: 10370131 Review.
-
Open access publishing.Emerg Infect Dis. 2004 Jul;10(7):1352. doi: 10.3201/eid1007.040122. Emerg Infect Dis. 2004. PMID: 15338570 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- Einstein A, Albert Einstein. The human Side - New Glimpses from his Archives. Princeton, New Yersey: Princeton University Press; 1979.
-
- Heisenberg W. Wandlungen in den Grundlagen der Naturwissenschaft. Stuttgart: S. Hirzel Verlag; 1959.
-
- Kayser K, Stauch G. Zeitgedanken und Spiegeldenken. Baden - Baden: Rendevous Verlag; 2000.
-
- Kayser K, Kayser G, Metze K. The concept of structural entropy in tissue-based diagnosis. Anal Quant Cytol Histol. 2007;29(5):296–308. - PubMed
-
- Trintscher KS. Biologie und Information - Eine Diskussion über Probleme der biologischen Thermodynamik. Leipzig: B. G. Teubner Verlagsgesellschaft; 1967.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

