MAVS forms functional prion-like aggregates to activate and propagate antiviral innate immune response
- PMID: 21782231
- PMCID: PMC3179916
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.06.041
MAVS forms functional prion-like aggregates to activate and propagate antiviral innate immune response
Erratum in
- Cell. 2011 Sep 2;146(5):841
Abstract
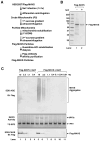
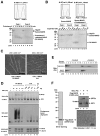
In response to viral infection, RIG-I-like RNA helicases bind to viral RNA and activate the mitochondrial protein MAVS, which in turn activates the transcription factors IRF3 and NF-κB to induce type I interferons. [corrected] We have previously shown that RIG-I binds to unanchored lysine-63 (K63) polyubiquitin chains and that this binding is important for MAVS activation; however, the mechanism underlying MAVS activation is not understood. Here, we show that viral infection induces the formation of very large MAVS aggregates, which potently activate IRF3 in the cytosol. We find that a fraction of recombinant MAVS protein forms fibrils that are capable of activating IRF3. Remarkably, the MAVS fibrils behave like prions and effectively convert endogenous MAVS into functional aggregates. We also show that, in the presence of K63 ubiquitin chains, RIG-I catalyzes the conversion of MAVS on the mitochondrial membrane to prion-like aggregates. These results suggest that a prion-like conformational switch of MAVS activates and propagates the antiviral signaling cascade.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




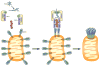
Comment in
-
A prion-like trigger of antiviral signaling.Cell. 2011 Aug 5;146(3):348-50. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.07.018. Cell. 2011. PMID: 21816270 Free PMC article.
-
Innate immunity: MAVS build-ups for defence.Nat Rev Immunol. 2011 Aug 12;11(9):570. doi: 10.1038/nri3050. Nat Rev Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21836618 No abstract available.
References
-
- Barbalat R, Ewald SE, Mouchess ML, Barton GM. Nucleic Acid Recognition by the Innate Immune System. Annu Rev Immunol 2010 - PubMed
-
- Chien P, Weissman JS, DePace AH. Emerging principles of conformation-based prion inheritance. Annu Rev Biochem. 2004;73:617–656. - PubMed
-
- Halfmann R, Lindquist S. Epigenetics in the extreme: prions and the inheritance of environmentally acquired traits. Science. 2010;330:629–632. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

