Rapid induction of apoptosis during Kinesin-5 inhibitor-induced mitotic arrest in HL60 cells
- PMID: 21782324
- PMCID: PMC3155259
- DOI: 10.1016/j.canlet.2011.05.024
Rapid induction of apoptosis during Kinesin-5 inhibitor-induced mitotic arrest in HL60 cells
Abstract
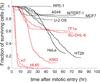
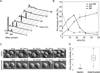
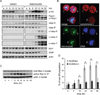
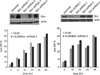
Small molecule inhibitors of Kinesin-5 (K5Is) that arrest cells in mitosis with monopolar spindles are promising anti-cancer drug candidates. Clinical trials of K5Is revealed dose-limiting neutropenia, or loss of neutrophils, for which the molecular mechanism is unclear. We investigated the effects of a K5I on HL60 cells, a human promyelocytic leukemia cell line that is often used to model dividing neutrophil progenitors in cell culture. We found K5I treatment caused unusually rapid death of HL60 cells exclusively during mitotic arrest. This mitotic death occurred via the intrinsic apoptosis pathway with molecular events that include cytochrome c leakage into the cytoplasm, caspase activation, and Parp1 cleavage. Bcl-2 overexpression protected from death. We probed mitochondrial physiology to find candidate triggers of cytochrome c release, and observed a decrease of membrane potential (ΔΨm) before mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization (MOMP). Interestingly, this loss of ΔΨm was not blocked by overexpressing Bcl-2, suggesting it might be a cause of Bax/Bak activation, not a consequence. Taken together, these results show that K5I induces intrinsic apoptosis during mitotic arrest in HL60 with loss of ΔΨm as an upstream event of MOMP.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The BH3 alpha-helical mimic BH3-M6 disrupts Bcl-X(L), Bcl-2, and MCL-1 protein-protein interactions with Bax, Bak, Bad, or Bim and induces apoptosis in a Bax- and Bim-dependent manner.J Biol Chem. 2011 Mar 18;286(11):9382-92. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.203638. Epub 2010 Dec 9. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21148306 Free PMC article.
-
Prometaphase arrest-dependent phosphorylation of Bcl-2 and Bim reduces the association of Bcl-2 with Bak or Bim, provoking Bak activation and mitochondrial apoptosis in nocodazole-treated Jurkat T cells.Apoptosis. 2014 Jan;19(1):224-40. doi: 10.1007/s10495-013-0928-1. Apoptosis. 2014. PMID: 24166139
-
BIMEL is a key effector molecule in oxidative stress-mediated apoptosis in acute myeloid leukemia cells when combined with arsenic trioxide and buthionine sulfoximine.BMC Cancer. 2014 Jan 15;14:27. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-27. BMC Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24428916 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic spindle assembly checkpoint activation causes myelosuppression and gastrointestinal atrophy.EMBO Rep. 2024 Jun;25(6):2743-2772. doi: 10.1038/s44319-024-00160-3. Epub 2024 May 28. EMBO Rep. 2024. PMID: 38806674 Free PMC article.
-
Mitosis and apoptosis: how is the balance set?Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2013 Dec;25(6):780-5. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2013.07.003. Epub 2013 Jul 23. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23890995 Review.
Cited by
-
Differential determinants of cancer cell insensitivity to antimitotic drugs discriminated by a one-step cell imaging assay.J Biomol Screen. 2013 Oct;18(9):1062-71. doi: 10.1177/1087057113493804. Epub 2013 Jun 20. J Biomol Screen. 2013. PMID: 23788527 Free PMC article.
-
A phase I, dose-escalation study of the Eg5-inhibitor EMD 534085 in patients with advanced solid tumors or lymphoma.Invest New Drugs. 2013 Dec;31(6):1530-8. doi: 10.1007/s10637-013-0026-9. Invest New Drugs. 2013. PMID: 24077982 Clinical Trial.
-
Papillary renal cell carcinoma: a clinicopathological and whole-genome exon sequencing study.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Jul 1;8(7):8311-35. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26339402 Free PMC article.
-
The proliferation rate paradox in antimitotic chemotherapy.Mol Biol Cell. 2012 Jan;23(1):1-6. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E10-04-0335. Mol Biol Cell. 2012. PMID: 22210845 Free PMC article.
-
Longitudinal tracking of single live cancer cells to understand cell cycle effects of the nuclear export inhibitor, selinexor.Sci Rep. 2015 Sep 24;5:14391. doi: 10.1038/srep14391. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26399741 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jackson JR, Patrick DR, Dar MM, Huang PS. Targeted anti-mitotic therapies: can we improve on tubulin agents? Nature Reviews Cancer. 2007;7:107–117. - PubMed
-
- Weaver BAA, Cleveland DW. Decoding the links between mitosis, cancer, and chemotherapy: The mitotic checkpoint, adaptation, and cell death. Cancer Cell. 2005;8:7–12. - PubMed
-
- Rieder CL, Maiato H. Stuck in Division or Passing through: What Happens When Cells Cannot Satisfy the Spindle Assembly Checkpoint. Developmental Cell. 2004;7:637–651. - PubMed
-
- Bergnes G, Brejc K, Belmont L. Mitotic kinesins: prospects for antimitotic drug discovery. Curr Top Med Chem. 2005;5:127–145. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

