Vibrio parahaemolyticus cell biology and pathogenicity determinants
- PMID: 21782964
- PMCID: PMC3384537
- DOI: 10.1016/j.micinf.2011.06.013
Vibrio parahaemolyticus cell biology and pathogenicity determinants
Abstract
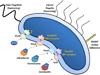
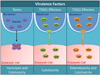
Vibrio parahaemolyticus is a significant cause of gastroenteritis worldwide. Characterization of this pathogen has revealed a unique repertoire of virulence factors that allow for colonization of the human host and disease. The following describes the known pathogenicity determinants while establishing the need for continued research.
Copyright © 2011 Institut Pasteur. Published by Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- McCarter L. The multiple identities of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol. 1999;1:51–57. - PubMed
-
- Yeung PS, Boor KJ. Epidemiology, pathogenesis, and prevention of foodborne Vibrio parahaemolyticus infections. Foodborne Pathog Dis. 2004;1:74–88. - PubMed
-
- Su YC, Liu C. Vibrio parahaemolyticus: a concern of seafood safety. Food Microbiol. 2007;24:549–558. - PubMed
-
- Joseph SW, Colwell RR, Kaper JB. Vibrio parahaemolyticus and related halophilic Vibrios. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1982;10:77–124. - PubMed
-
- Honda T, Iida T, Akeda Y, Kodama T. Sixty years of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Microbe. 2008;3:462–466.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

