TDP-43 functions and pathogenic mechanisms implicated in TDP-43 proteinopathies
- PMID: 21783422
- PMCID: PMC3202652
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molmed.2011.06.004
TDP-43 functions and pathogenic mechanisms implicated in TDP-43 proteinopathies
Abstract
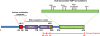
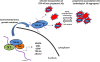
Given the critical role for TDP-43 in diverse neurodegenerative diseases including amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD-TDP), there has been a recent surge in efforts to understand the normal functions of TDP-43 and the molecular basis of dysregulation that occurs in TDP-43 proteinopathies. Here, we highlight recent findings examining TDP-43 molecular functions with particular emphasis on stress-mediated regulation of TDP-43 localization, putative downstream TDP-43 target genes and RNAs, as well as TDP-43 interacting proteins, all of which represent viable points of therapeutic intervention for ALS, FTLD-TDP and related proteinopathies. Finally, we review current mouse models of TDP-43 and discuss their similarities and potential relevance to human TDP-43 proteinopathies including ALS and FTLD-TDP.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Neumann M, et al. Ubiquitinated TDP-43 in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Science. 2006;314:130–133. - PubMed
-
- Barmada SJ, Finkbeiner S. Pathogenic TARDBP mutations in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia: disease-associated pathways. Rev Neurosci. 2010;21:251–272. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

