EGCG disaggregates amyloid-like fibrils formed by Plasmodium falciparum merozoite surface protein 2
- PMID: 21784057
- PMCID: PMC3157577
- DOI: 10.1016/j.abb.2011.07.008
EGCG disaggregates amyloid-like fibrils formed by Plasmodium falciparum merozoite surface protein 2
Abstract
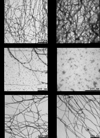
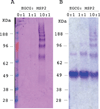
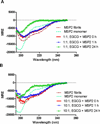
Merozoite surface protein 2 (MSP2), one of the most abundant proteins on the surface of Plasmodium falciparum merozoites, is a promising malaria vaccine candidate. MSP2 is intrinsically unstructured and forms amyloid-like fibrils in solution. As this propensity of MSP2 to form fibrils in solution has the potential to impede its development as a vaccine candidate, finding an inhibitor that inhibits fibrillogenesis may enhance vaccine development. We have shown previously that EGCG inhibits the formation of MSP2 fibrils. Here we show that EGCG can alter the β-sheet-like structure of the fibril and disaggregate pre-formed fibrils of MSP2 into soluble oligomers. The fibril remodelling effects of EGCG and other flavonoids were characterised using Thioflavin T fluorescence assays, electron microscopy and other biophysical methods.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

